The Grow Awards 2026 🏆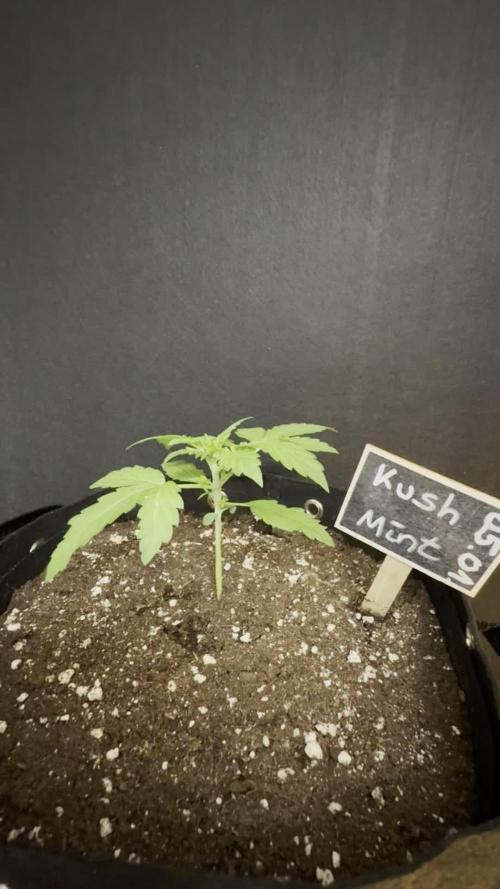 




































Likes
11
Share


@Sundancers
Follow
Die Kush Mint hat sich in den letzten zwei Wochen sehr gut entwickelt und deshalb haben wir sie am 13ten Tag getoppt. Düngetechnisch halten wir uns an den Düngeplan von Hy-Pro mit einem EC Wert von 1,2.
Sie zeigt keine Anzeichen von Überdüngung sondern wächst und streckt sich dem Licht schön entgegen. Die Genetik von Super Strain hat das Topping sehr gut vertragen und die Kush Mint wächst bereits am nächsten Tag weiter, als wäre nichts gewesen.
Das stimmt uns sehr positiv und freuen uns auf die nächste Grow-Woche mit ihr.
Wie findet ihr sie? 😎
Likes
87
Share


@Mrs_Larimar
Follow
2022-02-15
Sweet Puddin is maturating, Buds are swelling, Pisitls are changing slowly.
she has a good Number of weeks ahead, iam guessing for 4 more, we will see
She has grown wonderful, still happy and Green
Feedings once in the week , waterings every 3rd day or second day...depends in how thirsty she is
Visit her on Instagram, to create Likes for the Charity grow we do.
@Weedseedsexpress donates every Month 100 Euro for Woman in Need
If we reach enough Likes, they add 500 Euro in the end of the Growoff
so pls help us
Likes
10
Share


@nonick123
Follow
Día 35 (10/06) N/A
Día 36 (11/06) Se va a quedar un pequeño gran cogollo porque ya se ha detenido el strecht
Día 37 (12/06) N/A
Día 38 (13/06) Avanza la floración para estas pequeñas
Día 39 (14/06) Riego 150 ml de H20 pH 6,5
Día 40 (15/06) N/A
Día 41 (16/06) 500 ml de Té de Floración con Healthy Harvest 8 ml/L + Insect Frass 16 ml/L + Melaza 1 ml/L
💦Nutrients by Lurpe Solutions - www.lurpenaturalsolutions.com
🌱Substrate PRO-MIX HP BACILLUS + MYCORRHIZAE - www.pthorticulture.com/en/products/pro-mix-hp-biostimulant-plus-mycorrhizae
Processing
Likes
12
Share


@Adam420
Follow
Finally, she has flowered. 😫
15 weeks and to think I almost didn’t keep her.
Complete stop in growth and last leaves forming with pistils.
She’s showing her colors
Likes
63
Share


@Ferenc
Follow
Bonsais are being made😅😉
All good I have changed the soil so now they grow rapidly especially CBD Blue Shark. :)
I had no choice realised that using the same soil over and over is mitake. Big one.
Now it is okaz Purple Punches are in the 3rd week of flowering and Blue Shark is in veg i am not sure how long I will keep her like that.
Fertilization continues with the mix above on Monday, Wednesday, Saturday.
Day 39: I keep doing LST on CBD Blue Shark spreading her.
Likes
7
Share


@Growing_Spartan
Follow
I’m just giving water this week and she seems to be doing great, happy color and healthy stems! I’m going to be giving a tea in addition to their watering some time soon but other than that she’s been on cruise control 🤙
I did alternate my fans around in the tent to avoid wind burn and I also added a dehumidifier to my room that has my grow tent so I can gradually bring the RH down as needed. If there’s anything I can do to improve please, feel free to let me know!
Likes
4
Share


@Simon_Says_Smoke
Follow
This lady growing monstrously.
Growing at 10 nodes the plant is absolutely covered with growth.
Due to late LST this lady has gotten some length and has grown firm.
Likes
10
Share


@DogDoctorOfficial
Follow
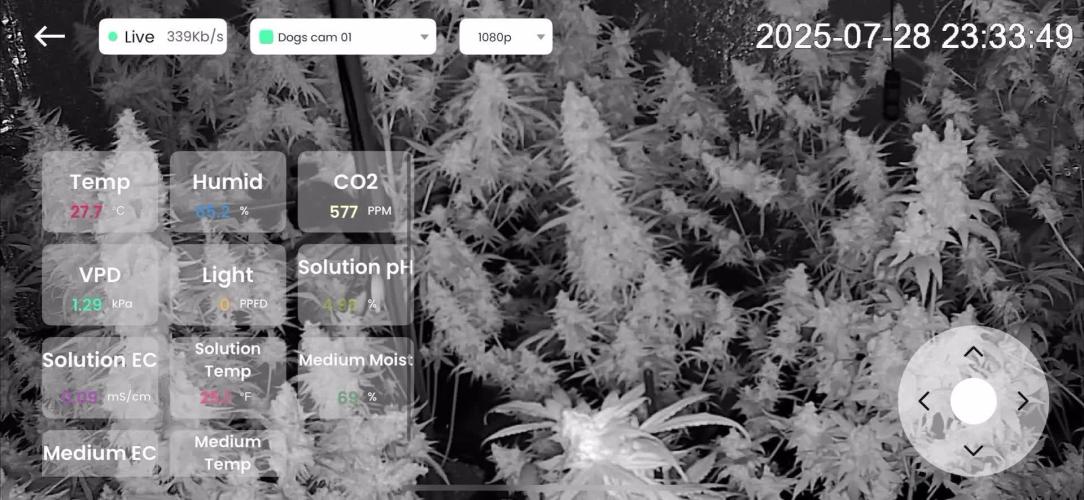
🌸 Week 6 Flower – The Weight of Beauty
The Mango Kush sisters have stepped fully into their bloom rhythm. By this stage, the playful stretch is over — it’s all about bud building, resin production, and flower density.
Both phenos are expressing themselves in unique ways, but they share one truth: they’re thriving, heavy, and ready to impress.
⸻
🌱 The State of the Sisters
• Pheno #1
The leader of the pack. Her buds are stacking densely, pistils still vibrant but starting to settle, and trichomes glisten under every angle of light. She’s asking for support now — her flowers are getting heavy and starting to bend the branches.
• Pheno #2
She may have started later, but she’s catching up beautifully. Her colas are filling in, and resin production is kicking in strong. She’s a little more delicate, but her structure is holding steady.
Educational takeaway: By Week 6, flower weight starts to increase dramatically. Support (stakes, nets, or ties) becomes essential to prevent branches from snapping under the load.
⸻
💧 Feeding & Nutrition
This week we continued with the bloom-focused recipe, keeping the balance tight and letting the boosters do their work. We also reintroduced Aptus All-in-One Liquid to provide a stable NPK boost after noticing slight deficiencies earlier.
Recipe Highlights:
• Aptus Regulator – 0.15 ml/L → Stress resistance & nutrient flow
• Aptus CalMag Boost – 0.25 ml/L → Calcium & magnesium support for heavy flowers
• Aptus All-in-One Liquid – 1 ml/L → Balanced NPK for mid-flower demand
• Plagron Power Buds – 1 ml/L → Pushing flower set further
• Plagron Sugar Royal – 1 ml/L → Enhancing aroma, resin, and resilience
• Plagron Green Sensation – 1 ml/L → Density and trichome support
Educational takeaway: Mid-flower is the peak of nutrient demand. The plant is working harder than ever — pushing energy into flower mass and resin production. Balanced feeding here prevents deficiencies while avoiding overfeeding.
⸻
🌡️ Environment Update
• Temps: Still running warm at times, peaking above comfort, but airflow and circulation are holding the canopy safe.
• Humidity: Fluctuating but managed, keeping VPD in a range where plants can still transpire efficiently.
• CO₂: Sitting steady, helping the plants maximize photosynthesis despite the slightly higher heat.
Observation: The girls are drinking daily now. With big flowers forming, water demand skyrockets. We water once soil moisture drops around ~20% to keep a steady rhythm.
⸻
💡 Light Orchestra
The Mango Kush beauties continue under their four-light ensemble:
• ThinkGrow Model One → canopy penetration
• ThinkGrow ICL-300s → filling mid-canopy shadows
• Future of Grow Black Series 600W → strong balanced spectrum
• Lumatek Zeus 465W Compact Pro → evening the footprint
The synergy here ensures every bud site, top to bottom, is touched by clean, even light. This is why we’re seeing full, consistent flower formation across the plants.
⸻
🔮 What to Expect (and What Not)
✅ Expect in Week 6–7:
• Buds gaining weight daily
• Trichome density increasing fast — the “frosty” look appearing
• Aroma starting to thicken noticeably in the grow room
• Support systems becoming necessary to hold the branches
❌ Don’t Expect Yet:
• Full aroma profile (still maturing)
• Final color changes (anthocyanins & fade come later)
• Harvest cues (pistils and trichomes are still developing)
Educational takeaway: Week 6 is “mid-bloom maturity” — the girls are past stretch, fully in flower, but not yet in their finishing stage. It’s a moment of steady building.
⸻
🌿 Closing Notes
The Mango Kush sisters are showing their genetics proudly. The Hindu Kush backbone gives strong structure and resilience, while the Mango side whispers hints of fruitiness when brushing past the canopy.
This week, their beauty is in their weight and glow — heavy flowers, sticky resin, and the quiet promise of what’s still to come.
⸻
💚 Grower’s Reflection
“This is the week where you realize the reward is real — the buds are heavy, the resin sparkles, and the plants begin to feel like they’re carrying little treasures. Support them, feed them, and above all, enjoy the process. Week 6 Flower is the calm before the storm of ripening.”
⸻
👉 Thank you for reading, friends. As always, join us on YouTube & Instagram to follow along with the Mango Kush journey, see the video updates, and catch all the behind-the-scenes content.
📌 P.S. Troubleshooting Leaf Spots – CalMag & Mid-Flower
This week we noticed some spotting on leaves, a classic mid-flower signal that calcium and magnesium demand is peaking. Why now?
• Bigger buds = higher demand. As flowers bulk up, the plant moves Ca/Mg rapidly into developing cells.
• Warm temps increase transpiration. High heat makes the plant drink more, sometimes pulling nutrients unevenly.
• Solution: We adjusted by reintroducing Aptus All-in-One Liquid for extra NPK support and kept CalMag Boost steady to buffer deficiencies.
🌱 Educational takeaway: In mid-flower, even healthy plants can show light spotting. The key is to respond early with balanced feeding rather than panic or heavy overdoses.
🔮 Looking Ahead – Week 7 Preview
As we move into Week 7 Flower, here’s what to keep an eye on:
✅ Trichome explosion – expect resin glands to multiply, giving that first real frost on sugar leaves.
✅ Aroma awakening – terpenes will become more noticeable; brushing past the canopy will release fruity, kushy hints.
✅ Bud hardening – calyxes swell and flowers get denser; staking/support becomes more urgent.
❌ Don’t expect maturity yet – pistils will still be white, and trichomes mostly clear/cloudy. Harvest signs come later.
Educational takeaway: Week 7 is the “icing phase” — the weight is already there, but the sparkle, smell, and stickiness take center stage.
📲 Don’t forget to Subscribe and follow me on Instagram and YouTube @DogDoctorOfficial for exclusive content, real-time updates, and behind-the-scenes magic. We’ve got so much more coming, including transplanting and all the amazing techniques that go along with it. You won’t want to miss it.
• GrowDiaries Journal: https://growdiaries.com/grower/dogdoctorofficial
• Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/dogdoctorofficial/
• YouTube: https://www.youtube.com/@dogdoctorofficial
There’s a new series blooming and it’s more than just plants. It’s about process, patience, and paying attention.
⸻
Explore the Gear that Powers My Grow
If you’re curious about the tech I’m using, check out these links:
• Genetics, gear, nutrients, and more – Zamnesia: https://www.zamnesia.com/
• Environmental control & automation – TrolMaster: https://www.trolmaster.eu/
• Advanced LED lighting – Future of Grow: https://www.futureofgrow.com/
• Root and growth nutrition – Aptus Holland: https://aptus-holland.com/
• Nutrient systems & boosters – Plagron: https://plagron.com/en/
• Soil & substrate excellence – PRO-MIX BX: https://www.pthorticulture.com/en-us/products/pro-mix-bx-mycorrhizae
• Curing and storage – Grove Bags: https://grovebags.com/
⸻
We’ve got much more coming as we move through the grow cycles. Trust me, you won’t want to miss the next steps, let’s push the boundaries of indoor horticulture together!
As always, this is shared for educational purposes, aiming to spread understanding and appreciation for this plant. Let’s celebrate it responsibly and continue to learn and grow together.
With true love comes happiness. Always believe in yourself, and always do things expecting nothing and with an open heart. Be a giver, and the universe will give back in ways you could never imagine.
💚 Growers love to all 💚
Likes
6
Share


@gabigarcia
Follow
It is already the fifth week of vegetation and they are incredible, the autoflowering ones above all are beautiful and it is also noticing how the critical x are growing little by little. ! (Any questions, or any advice you can give me leave it in the comments, I also speak Spanish)
Likes
4
Share


@adam_pawloski87
Follow
@twenty20mendocino A-Team R&D Update ~ Let’s Go day 24 of flower 🌸 an we are looking amazing! Ladies are starting to stack an oh my we getting a lot of frost going on! starting to get some gassy stanky notes of em too😍 ! We are only into week 4 ladies an gents we still got a few weeks to go of stacking! Keep your eyes peeled for next week’s update yall , peace love a positive to all y’all , an have an amazing productive day ! Cheers an blaze on !!
Likes
8
Share


@HeartStrong_Garden
Follow
Pretty much on autopilot right now. I've just been filling the water reservoir when needed. Last night I did a top watering to try to help push them through the last couple days. It shouldn't be much longer now. Pretty much all cloudy trichomes with hints of amber. Once I see a little more amber I'll chop. The topped girl will probably be harvested first, I think she's a little ahead of number 2.
Likes
11
Share


@Sawyer_grow
Follow
Hello guys !
I'm back finally ! couldn't update my diares for weeks :'(
What happened during this time ? A LOT ! we have now switched into flowering stage and the plant already start her flowering stretch.
She wom almost 5 CM on all colas and I think she will keep going for another week. Usualy the flowering stretch take around 2weeks.
She also start to drink much more than during her veg stage of course. Now it's around 1L every 24hrs.
Hope you like it.
Take care
Likes
5
Share


@Willy_Balls
Follow
Noticed runoff ec getting high in week 4
Increased runoff to lower it below 3.
Plants drink around 1.5 l a day each.
On 14.06 I gave them bioenhacer, trikologic and biofuse mix.
60 l of nutrient solution is sufficient for around 3 days.
Likes
138
Share


@DogDoctorOfficial
Follow
So its time for a second run with the MARSHYDRO TSW-2000, for this run i will be running 2 clones from Gorilla Blue that came out out off a test seed i did and kind a love it so much that its time for round 2 out of it 😆 , i will be running APTUSHOLLAND nutrient line, something I'm doing for a couple of years now, but now with they're support, with for me was amazing since i already believe 101% on all of the APTUSHOLAND line 🙌🙌🙌🙏🙏🙏💚💚💚 shout out to AptusHolland 💚💚💚🙌🙌🙌🙏🙏🙏✊✊✊
I am reusing my soil from previous run since i take such good care of it with APTUSHOLLAND organic/mineral nutrients, i did add some magic to the soil ,this will help my girls and the living matter in it. I ad APTUSHOLLAND All in one pallets, MycorMix and Micromix and for the first waterings i will be adding all in one liquid all so, just until the solid amendments break down and from there on i will be giving them only water with some microbial help to keep my soil alive and in shape.
Thank you MARSHYDRO and APTUSHOLLAND for having faith in my love for growing , lets make magic together 🙏🙏🙏
Genetics - Gorilla Blue - Advanced seeds
Grow tent - MARSHYDRO 4x4
Ligth - MARSHYDRO TSW 2000 @ 100%
Food - HAPTUS HOLLAND
Filter - vanguard hydroponics Falcon Filters
Extraction - 2 x vanguard hydroponics 280m3h
Extraction control - SMSCOM Smart MK2
All i grow is medicine for myself, for me and for my best friend with is me 😆 nothing to sell, so don’t even ask 😅💚💚💚
All info and full product details can be find in can find @
https://www.mars-hydro.com/grow-tent
https://www.mars-hydro.com/led-grow-light/mars-ts-series-led-grow-light/mars-tsw-2000-led-full-spectrum-hydroponic-led-grow-light
https://marshydro.eu/ DISCOUNT CODE - DOGDOCTOR 💚💚💚🙏🙏🙏💚💚💚
https://marshydroau.com/
https://aptus-holland.com/
#marshydro #aptus #aptusplantteck #aptusgang #aptusfamily #aptustrueplantscience #inbalancewithnature #trueplantscience #growerslove
With true love comes happiness 💚🙏 Always believe in your self and always do things expecting nothing and with an open heart , be a giver and the universe will give back to you in ways you could not even imagine so 💚💚💚
More info and updates @
https://growdiaries.com/grower/dogdoctor
https://instagram.com/dogdoctorofficial
https://youtube.com/channel/UCR7ta4DKLFMg2xxTMr2cpIg
💚💚💚Growers love to you all 💚💚💚
Likes
10
Share


@420_Vamp
Follow
Steady as she goes..... 🎶🎶
I put the ladies on the flip a Week earlier than I anticipated on the schedule matrix
. I thought to myself best just get them done. 10 weeks from seed Vegging is enough. 3 weeks of that I count as seedling so 7 weeks Vegging.
Started the flip the night before rather than on the day.
With my micro I inspected the lady Phenom C on the right and 3 days at 12. Shows a tiny flower forming.
I haven't fed them this week so far that's why it's not been logged.
But after some experiments. with the TDS metre. I come up with a solution of 2ml grow and 5ml bloom for weeks 1 and 2. I have to say that the grow stuff is far more potent TDS wise than the bloom
The bloom is far weaker
the TDS value is 900ppm with that 2 week solution.
My 3-7 week solution is 2ml grow 5ml bloom and 2ml plant magic ok booster lands at 1300
I could maybe knock back the bloom slight by a ML but let's see.
Processing
Likes
23
Share


@TheFairyBudMother
Follow
6-10 I’m assuming this is calcium or potassium deficiency?
6-12 Pot felt light. Watered/fed & defoliated. Took a few scalps and wired a few branches to the flower grid to spread them more evenly.
Likes
31
Share


@TragicTerps
Follow
Day 1 has no updates, Temps are optimal now and the girls are thriving in late flower. Lights remain 100% power and I expect the buds to continue to develop and stack on some weight. For a first grow I feel this has been a successful experiment and experience.
Day 3 of week 10 Plant A is cut and drying, I chose to cut it because the increase in unexpectedheat almost sent it back into veg. The tricomes were cloudy mainly so I figured it would be best to chop it and not risk it turning hermie. Had really dense buds will update the dried weight.
Likes
57
Share


@Kmikaz420
Follow
Je passerai demain pour remplir les commentaires j ai actuellement pas mal de travail à couper/trimer 😀 et le tous sur une jambe ..merci de votre compréhension..
Et voilà une de moins la 1ere dos-i-dos de batney à été couper et cette plante a fais les tête les plus compacte et dur que j ai jamais vue je pense être pas loin de la vérité en disant qu il doit y avoir 120g.. 150g sec sur cette seul plante ;) affaire à suivre ..je rajouterai des photos demain )les photos avec flasch ne rendent pas service aux plantes;)
Enfin on t est la recolte !!!! La strawberry x gorrila seche avec les dos i dos et la gorrilla x purple punch
Les 2 cherry cola ont été trimer et mis en bocale pour curring
Cherry cola 1= 88g
Cherry cola 2= 83g
Gorrila x purple punch = 40g
J ai pas mal de travail je mettrais le journal à jour au fur et à mesure ;)
Likes
14
Share


@Kakui
Follow
23 Noviembre: Se realizó el segundo apical, defoliacion, y Lollipop. Estamos a un par de días de iniciar el ciclo 12/12 de floración y pasar a riego Generativo.

















