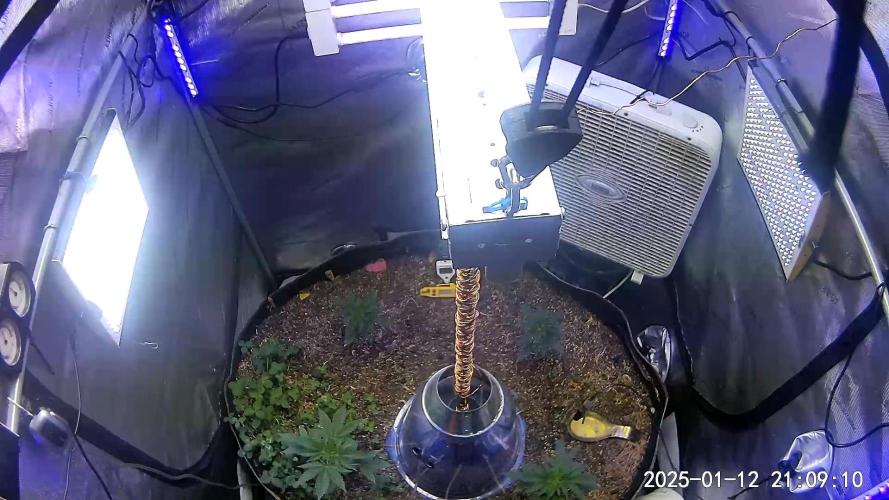
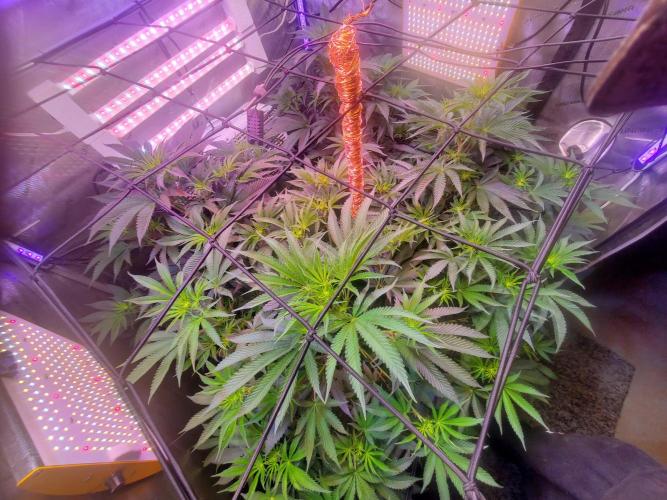
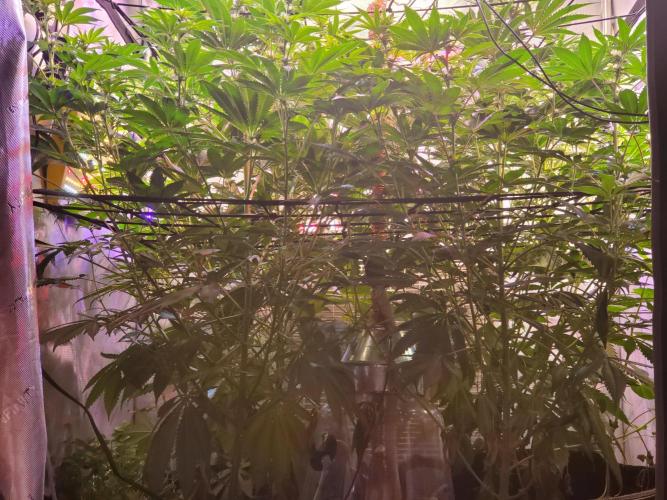
The Grow Awards 2026 🏆 
























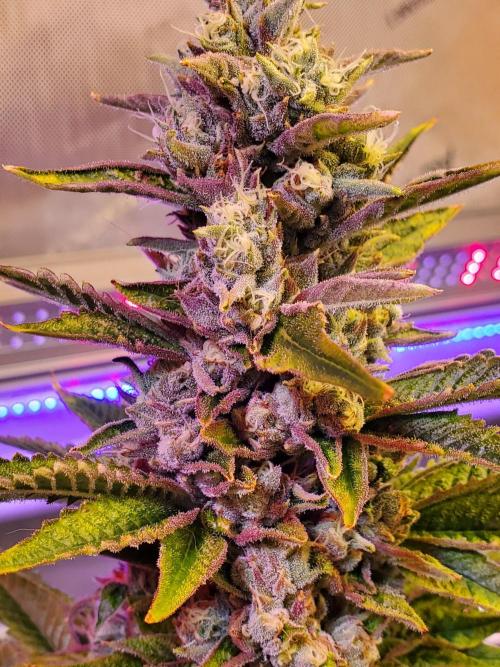
"Lemon Cherry Gelato" C#11

Cond
14,000 btu
Hisense
Soil
soil
Indoor
Room Type
379 liters
Pot Size
Start at Harvest
G
Germination1y ago
Nutrients 1

RAW Phosphorus
0.063 mll
Ultraviolet Germination began on the 25th, and the seed was placed into the final pot on January 1st, 2025.
6 likes
2 comments
Share
Used method
Other
Germination Method
2
Week 2. Vegetation1y ago
18 hrs
Light Schedule
23 °C
Day Air Temp
6.5
pH
250 PPM
TDS
65 %
Air Humidity
18 °C
Substrate Temp
19 °C
Night Air Temp
378.54 liters
Pot Size
20.32 cm
Lamp Distance
1054 PPM
CO₂ Level
Nutrients 3

RAW Grow
0.16 mll

Microbes Grow Stage
0.16 mll

RAW Humic Acid
1.3 mll
Ultraviolet Carotenoids absorb light in blue-green region of the visible spectrum, complementing chlorophyll's absorption in the red region. They safeguard the photosynthetic machinery from excessive light by activating singlet oxygen, a oxidant formed during photosynthesis. Carotenoids also quench triplet chloryphyll, which can negatively affect photosynthesis, and scavenge reactive oxygen species (ROS) that can damage cellular proteins. Additionally carotenoid derivatives signal plant development and responses to environmental cues. They serve as precursors for the biosynthesis of phytohormones such as abscisic acid () and strigolactones (SLs). These pigments are responsible for the orange, red, and yellow hues of fruits and vegetables, while acting as free scavengers to protect plants during photos.
Beta-carotene is most prevalent provitamin A carotenoid, commonly found in orange and yellow fruits and such as carrots, sweet potatoes, and mangos. Additional carotenoids include lycopene, lutein, and zeaxanthin, which possess antioxidant and photoprotective properties. In, Vitamin A exists in the form of carotenoids, are pigments responsible for. Vitamin A is classified as a soluble vitamin.
Vitamin B plays a crucial role in plant growth and development, serving as a coenzyme in numerous metabolic reactions underpin plant growth and maintenance. It aids in metabolizing essential nutrients for growth and development and enhances their responses to biotic and abiotic stress. Vitamin B supports root development, reducing transplant shock, and promotes shoot growth, particularly in slow-growing plants
Vitamin B1, also as thiamine diphosate, is integral to pathways such as glycolysis and the tricarboxylic acid cycle. Vitamin B3, or nicotinamide/niacin, acts as a biostimulant, improving growth and. Vitamin B6 functions as an antioxidant and cofactor, playing a significant role in plant.
Vitamin C, referred to as ascorbic acid is another vital nutrient for plants, aiding in growth and offering protection against excessive light. It serves as a red buffer, crucial for regulating synthesis. Vitamin C assists enzymes involved in photosynthesis, hormone production, and the regeneration of antioxidants. Furthermore, it acts as coenzyme in the xanthophyll cycle, converting energy into heat to protect plants light-induced damage.
RAW GROW is a thoroughly tested blend all RAW Soluble plant nutrients essential elements, and supplements as an optimal all base "Grow" horticultural fertilizer. It is utilized throughout the entire vegetative stage. Its composition includes plant protein hydrolysate, mono potassium phosphate, potassium sulfate, cane molasses, sodium borate, copper sulfate, iron DTPA, magnesium sulfate, manganese sulfate sulfate, and azomite. Additionally, it contains non- food ingredients such as humic acids derived from leonardite and peat, kelp (Ascophyllumosum silicon dioxide derived diatomite, and yucca extract. Seedlings or young plants can be fed with 200-400PpM, teenage plants with maturing root zone can be given 350-550 PPM, and mature plants require 600-1000 PPM. By closely monitoring plant growth and adjusting feeding levels, one can an understanding of the quantity to provide When starting, it is advisable to err on the side of caution and adopt a "less is more" approach.
One-thousandth of a gram is one milligram, and 1000 ml is one liter, so 1 ppm = 1 mg per liter = mg/Liter. PPM is derived from the fact that the density of water is taken as 1kg/L = 1,000,000 mg/L, and 1mg/L is 1mg/1,000,000mg or one part in one million. One-thousandth of a gram is one milligram, and 1000 ml is one liter, so 1 ppm = 1 mg per liter = mg/Liter. PPM is derived from the fact that the density of water is taken as 1kg/L = 1,000,000 mg/L, and 1mg/L is 1mg/1,000,000mg or one part in one million.
7 likes
comments
Share
3
Week 3. Vegetation1y ago
30.48 cm
Height
18 hrs
Light Schedule
23 °C
Day Air Temp
6.2
pH
500 PPM
TDS
65 %
Air Humidity
18 °C
Substrate Temp
21 °C
Night Air Temp
378.54 liters
Pot Size
600 PPM
CO₂ Level
Nutrients 7
Atlantis
3.963 mll
Homebrew
0.33 mll

RAW Kelp
0.33 mll
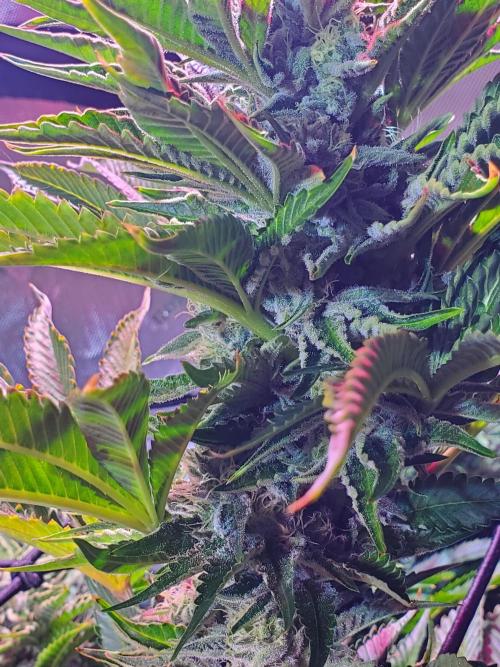
Ultraviolet Perhaps I will finally achieve my 13-finger leaf. I've reached 11 a few times, but a 13-finger leaf remains elusive. Someday maybe.
VPD is designed for optimal growth, promoting rapid development. However, during the stages of flowering, the focus shifts from growth to ripening. Lower humidity ensures a safer finish and more preseered results, it is advisable to use the leaf temperature instead of air temperature, as VPD primarily reflects the difference between the water vapor pressure at the leaf surface and the air. Leaf surface temperature (LST) is a few degrees below ambient. During the day, transpiration occurs full capacity, with its rate directly influencing cooling level the due to the endothermic process of leaf cooling.
Daytime VPD should range between -1°F and -5°F, depending on the rate of transpiration. VPD is more accurately determined using leaf surface temperature rather than ambient temperature.
Vitamin A (retinol, retinoic acid): The body converts provitamin and cartenoids (orange/yellow pigments such as beta-carotene), into vitamin A retinol).
B1 (thiamine):
B2 (riboflavin):
B3niacin):
B5 (pantothenic acid):
B6 (pyridoxine):
B7 (otin):
9 (folate):
B12 (cobalamin):C (ascorbic acid):
For six hours during the night, there is continuous UVB exposure purely for experimental purposes. Although none of the 280nm wavelength reaching the plant falls within Photo Active Radiation (PAR), I have been intending to test this for some time. During the previous growth cycle, I experimented with UVA, which was still drifting into PAR on the tail end of the curve, maintaining light levels above moonlight at 0.1 PPFD. This time, I am testing 280nm.
Plants were subjected to various UV-B irradiance levels every third night for either 9 or 18 minutes, every night for either 3 or 6 minutes, or three times nightly or 2. Consequently, over time, all plants received an equivalent cumulative dose of UV-B, resulting in 90% to 99% reduction in powdery mildew severity compared to untreated in both crops.
https://apsjournals.apsnet.org/doi/10.1094/PDIS-12-15-1440-REhttps://apsjournals.apsnet.org/doi/10.1094/PDIS-12-15-1440-RE
Not currently disrupting the plant's ability to detect the night cycle shift, UVB being on at night allows it to react as it would in complete darkness. In contrast, during the last grow with UVA, plants were clearly prevented from initiating the relaxed state expected approximately 30 minutes before lights out. It appeared as though heliotropism caused them to direct themselves toward each UVA light individually, making them seem as if they were dancing in circles throughout the night. Considering how close UVA is to blue light, it is not surprising as cryptochromes function as blue and ultraviolet-A photoreceptors, while UVR8 is specific to UVB alone.
As the vapor pressure deficit (VPD) increases and the stomata become smaller, the uptake of CO2 decreases. Higher VPD leads to faster transpiration, as the difference in vapor pressure between the leaf and the air becomes greater. With increased VPD and transpiration, the roots absorb more nutrients as the plant operates as a cohesive system akin to plumbing. However, elevated VPD also imposes greater forces on the plant, from the tip to the roots, resulting in increased stress.
Transpiration is the process by which plants release water through the leaves. a passive mechanism that plays a significant role in the water cycle.
Plants get water and nutrients from the soil through their roots, and these are transported through the plant's tissues to the leaves. Transpiration removes heat from the air, cooling the plant, and returns water to the atmosphere, contributing to the water cycle. The water absorbed by the roots also contains essential nutrients necessary for plant growth.
Temperature: Elevated temperatures enhance the rate of transpiration.
Light intensity: Increased light intensity accelerates the rate of transpiration.
Wind speed: Higher wind speeds amplify the rate of transpiration.
Humidity: Greater humidity reduces the rate of transpiration.
Carbon dioxide levels: Elevated carbon dioxide levels diminish the rate of transpiration.
Evapotranspiration: This refers to the combined processes of transpiration and evaporation.
Stomatal transpiration: Represents one of the three primary types of transpiration.
Guttation is a process that occurs when absorb excessive water the soil and are unable to release it through their stomata. This results in pressure forcing sap out from edges or tips of the leaves, creating the appearance of droplets resembling a tiara
Perspiration is the process of releasing sweat from sweat glands in the skin. It's also known as sweating.
Plants "sweat" through a process called transpiration. Transpiration is the process by which water evaporates from plant leaves, cooling the plant and the surrounding air.
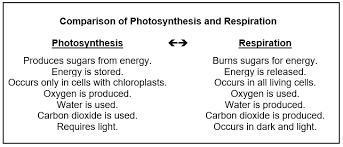
Respiration refers to the process of metabolizing sugars to generate energy, whereas transpiration involves the release of water vapor. Both processes occur in plants and entail the exchange of gases with the environment.
Through respiration, plants produce the energy necessary for growth, reproduction, and other vital functions. During this process, plants utilize oxygen and stored sugars to generate carbon dioxide and water. Respiration occurs in all parts of the plant, including roots, stems, and leaves.
Transpiration, on the other hand, is the release of water vapor through the stomata in leaves. This process dissipates the heat generated by metabolic activities such as photosynthesis and respiration. Additionally, transpiration contributes to adding water to the atmosphere.
When cannabis is in the drying process, water is regarded as evaporating rather than transpiring, as the plant, once harvested, lacks the active root system required for movement of water through the plant to take place. Instead, the remaining moisture merely evaporates from the plant's surface into the surroundings.
Water absorbed by the roots is transported throughout the plant via transpiration, a process involving the ejection of water vapor through the stomata in the leaves. Approximately 90 percent of the water entering the plant is utilized in this process, while the remaining 10 percent is used for photosynthesis and cell growth. Transpiration serves three essential functions.
The movement of minerals from the root (via the xylem) and sugars (products of photosynthesis) throughout the plant (via the phloem) is facilitated by water, which is both a solvent and a medium of transport.
Cooling – Approximately 80 percent of the cooling effect provided by a shade tree results from the evaporative cooling effects of transpiration, both plants and humans.
Tugor pressure – Water inflates tugor pressure in cells, much like air inflates a balloon, giving non-woody plant parts structure. Turgidity is vital for maintaining plant stiffness and upright posture, offering a competitive advantage in accessing light. It is crucial for the operation of guard cells, which water loss and carbon dioxide uptake by surrounding the stomata. Additionally, tugor pressure provides the force necessary as a counter pressure to push roots through the soil.
Water movement in plants is influenced by osmotic pressure and capillary action. Osmotic pressure occurs when water flows through aable membrane toward areas of higher salt concentration. This process continues the salts are diluted resulting in equal concentrations on both sides of the membrane.
A well-known example involves pouring salt on a slug. The high salt concentration outside the slug water from its body to moves across its skin membrane, leading to dehydration and death. A similar principle applies when gargling salt water to kill bacteria causing a sore throat.
In gardening, issues such as fertilizer burns and dog urine spots on lawns illustrate related problems. When the concentration of the soil’s water exceeds that in the roots, water flows from the roots into the soil to dilute the concentration. Therefore, what actions should be taken if fertilizer is accidentally overapplied to a lawn?
Cooling – 80-90 percent of water pulled through roots is used for transpiration; most of the rest is used for respiration.
During the day, while both transpiration (water loss) and respiration (energy production) occur in plants, transpiration is generally a more significant process than respiration, especially in terms of water movement and loss.
Capillary action refers to the chemical forces that move water as a continuous film rather than as individual molecules. Water molecules in the soil and in the plant cling to one another and are reluctant to let go. You have observed this as water forms a meniscus on a coin or the lip of a glass. Thus, when one molecule is drawn up the plant stem, it pulls another one along with it. These forces that link water molecules together can be overcome by gravity. Water in the roots is pulled through the plant by transpiration (loss of water vapor through the stomata of the leaves). Transpiration uses about 90 percent of the water that enters the plant. The other 10 percent is an ingredient of photosynthesis and cell growth.
7 likes
comments
Share
4
Week 4. Vegetation1y ago
38.1 cm
Height
18 hrs
Light Schedule
26 °C
Day Air Temp
6.8
pH
650 PPM
TDS
60 %
Air Humidity
18 °C
Substrate Temp
21 °C
Night Air Temp
378.54 liters
Pot Size
800 PPM
CO₂ Level
Ultraviolet When lightning strikes, it tears apart the bond in airborne nitrogen molecules. Those free nitrogen atoms N2 nitrites then have the chance to combine with oxygen molecules to form a compound called nitrates N3. Once formed, the nitrates are carried down to the ground becoming usable by organisms. Will it react with the oxygen in the air spontaneously, the answer is no. The mixture is chemically stable indefinitely. A mixture with air near the release point can be ignited, but if this does not happen then when its concentration gets below 4% it will be unable to carry a flame.
A nitrite (NO2) is a nitrogen atom bonded to only two nitrogen atoms. Very strong bond.
A nitrate (NO3) is a nitrogen atom bonded to three oxygen atoms. Weaker bond
7 likes
2 comments
Share
5
Week 5. Vegetation1y ago
53.34 cm
Height
18 hrs
Light Schedule
26 °C
Day Air Temp
6.8
pH
650 PPM
TDS
60 %
Air Humidity
18 °C
Substrate Temp
21 °C
Night Air Temp
378.54 liters
Pot Size
800 PPM
CO₂ Level
Nutrients 2

RAW Amino Acids
0.33 mll

RAW Enzymes
0.33 mll
Ultraviolet Noticeable stalling of vertical growth around 5-600ppfd at 18 hours, apical dominance not broken but side stems shooting up to around same PPFD range then slows to stay just under apex.
Amended soil with biochar charged to ratio roughly 40:10:5 Ca:Mg:K.
Nitrogen is a nutrient that can be held in soil through cation exchange, a process that measures how much nitrogen soil can store without leaching.
(CEC) A measure of how much cations, or positively charged ions, a soil can store. CEC is a soil texture indicator, with lower CECs indicating sandy soils and higher CECs indicating denser soils.
Nitrogen can be found in soil in different forms, including nitrate ((NO_{3}^{-})) and ammonium ((NH_{4}^{+})). Nitrogen mobility The mobility of nitrogen depends on its form. Nitrate is very mobile in soil water and can be easily leached, while ammonium is held on cation exchange sites and is not susceptible to leaching.
To estimate how much nitrogen a soil can store, you can multiply its CEC by 10. For example, a CEC of 12 means it can store 120lbs of nitrogen. Understanding how much nitrogen a soil can hold is important for managing soil fertility and crop yields.
(CEC) of organic soil is typically between 250 and 400 milliequivalents per 100 grams of soil ((meq/100g)). CEC is a measure of how well soil retains substances applied to it. Organic matter: The amount of organic matter in soil affects its CEC. Soils with more organic matter have more negative charges, which increases their CEC. Soils with more clay have more negative charges, which increases their CEC.The pH level of soil affects its CEC. Type of clay: The type of clay in soil affects its general, soils with larger amounts of clay or organic matter have more negative charges and therefore a higher CEC than ones without.
Soil testing labs can estimate CEC by measuring calcium, magnesium, and potassium in the soil, and then estimating the amount of exchangeable hydrogen. A direct method is to replace the cations on the soil's exchange sites with a single cation, then measure how much of that cation was. In general, soils with larger amounts of clay or organic matter have more negative charges and therefore a higher CEC than ones with Capacity -
CEC is important because it affects how well soil holds onto herbicides and nutrients. Soils with higher CECs have greater water of Soil Cation Exchange Capacity (CEC) - Purdue ExtensionThe direct method is to replace the normal mixture of cations on the exchange sites with a single cation such as ammonium (NH4+),
In general, soils with larger amounts of clay or organic matter have more negative charges and therefore a higher CEC. Adding organic matter like compost, mulch, or manure can increase CEC. Adding lime to acidic soils can raise the pH and increase CEC. It is commonly said that an ideal soil is 50% pore space (water + air), 5 % organic matter, and 45% minerals. The ideal mixture for plant growth is called a loam and has roughly 40% sand, 40% silt and 20% clay. Cation exchange capacity (CEC) is a measure of how many positively charged ions, or cations, a soil can hold and exchange. CEC is a reflection of a soil's fertility and ability to supply nutrients to plants.
Soil particles have negative charges, which attract positively charged cations.
Cations are not tightly held to the soil particles, so they can be exchanged with other cations in the soil water.
Plant roots remove cations from the soil solution, which are then replaced by cations from the soil particles.
Clay and organic matter particles in soil have negative charges, which attract and hold cations. Organic matter has more exchange sites than clay.
As soil pH increases, the number of negatively charged sites on colloids increases, which allows the soil to hold more cations.
CEC is measured in millequivalents per 100 grams of soil ((meq/100g)). A meq is the number of ions that total a specific quantity of electrical charges.
Soils with low CEC need frequent, short irrigation, while soils with high CEC need less frequent, longer irrigation. Organic matter has a very high CEC ranging from 250 to 400 meq/100 g (Moore 1998). Because a higher CEC usually indicates more clay and organic matter is present in the soil, high CEC soils generally have greater water holding capacity than low CEC soils.
https://www.extension.purdue.edu/extmedia/ay/ay-238.html
Percent base saturation (BS) is the percentage of the CEC occupied by the basic cations Ca2+, Mg2+ and K+. Basic cations are distinguished from the acid cations H+ and Al3+. At an approximate soil pH 5.4 or less, Al3+ is present in a significantly high concentration that hinders growth of most plant species, and the lower the soil pH, the greater the amount of toxic Al3+. Therefore, soils with a high percent base saturation are generally more fertile because:
1 They have little or no acid cation Al3+ that is toxic to plant growth.
2 Soils with high percent base saturation have a higher pH; therefore, they are more buffered against acid cations from plant roots and soil processes that acidify the soil (nitrification, acid rain, etc.).
3 They contain greater amounts of the essential plant nutrient cations K+, Ca2+ and Mg2+ for use by plants.
The percentage base saturation is expressed as follows:
%BS = [(Ca2+ + Mg2+ + K+)/CEC] × 100
Depending on soil pH, the soil's base saturation may be a fraction of CEC or approximately equal to CEC. In general, if the soil pH is below 7, the base saturation is less than CEC. At pH 7 or higher, soil clay mineral and organic matter surfaces are occupied by basic cations, and thus, base saturation is equal to CEC. Figure 2 illustrates the relative amount of cations retained on soil surfaces at various soil pH levels.
A soil's CEC affects fertilization and liming practices. For example, soils with high CEC retain more nutrients than low-CEC soils. With large quantities of fertilizers applied in a single application to sandy soils with low CEC, loss of nutrients is more likely to occur via leaching. In contrast, these nutrients are much less susceptible to losses in clay soils.
Crop production releases acidity into soil. Soil pH will decrease more due to crop production on low CEC soils. High CEC soils are generally well buffered such that pH changes much less from crop production. Therefore, sandy soils low in CEC need to be limed more frequently but at lower rates of application than clay soils. Higher lime rates are needed to reach an optimum pH on high CEC soils due to their greater abundance of acidic cations at a given pH.
The average CEC of coco coir is between 40-100 (meq/100g)
Organic matter has a very high CEC ranging from 250 to 400 meq/100 g
Cation exchange capacity (CEC) is a critical soil property that directly influences nutrient availability and plant growth. The determination of CEC can be achieved through direct measurement or by summation methods, with the latter encompassing techniques such as the Mehlich-3 (M3) and ammonium acetate (AA) extractions (1). Direct measurement of CEC involves the displacement of exchangeable cations on soil particles with a solution containing a known concentration of an index cation, typically ammonium (NH4+), and subsequent quantification of the NH4+ adsorbed. This method offers precise results but requires specialized laboratory equipment and is time-consuming (2). In contrast, summation methods involve the extraction of cations from soils with specific reagents, with the extracted cations subsequently quantified. The M3 extraction uses a mixture of ammonium fluoride (NH4F) and nitric acid (HNO3) to release exchangeable cations, while AA is utilized to displace cations (3). Summation methods are quicker and more convenient for routine soil analysis but may overestimate CEC as they also extract non-exchangeable cations from the soil (3). Therefore, the choice between direct measurement and summation methods for CEC determination depends on the research objectives and available resources. Direct measurement is preferable when high accuracy is required, whereas summation methods like M3 and ammonium acetate extractions are suitable for rapid assessment of CEC in routine soil analyses. Moreover, determining CEC is valuable for understanding the relationship between key cations (K, Ca, and Mg) in soil and their impact on plant uptake and development.
Overall, using practical soil nutrient extraction and summation methods for CEC determination offers benefits such as cost-efficiency, accessibility, speed, ease of implementation, versatility, and the ability to assess predictive accuracy compared to more complex techniques like the direct measurement method (4). Furthermore, CEC via summation represents the soil’s capacity to hold and exchange cations and helps assess nutrient availability, cation competition, and potential imbalances in these essential nutrients.
Notwithstanding, the assumption that increasing soil CEC is always beneficial requires nuanced consideration. Particularly in the context of tropical soils, where H+Al (hydrogen and aluminum) constitutes a significant portion of the soil CEC, a sole focus on increasing CEC might not be advantageous if the nutrient balance is skewed towards detrimental elements like Al (5–7). Moreover, a global perspective underscores the fact that excessively high CEC does not necessarily guarantee optimal soil fertility (8). High CEC soils may indicate a propensity for nutrient imbalances, where certain nutrients may be overly abundant or deficient. For instance, soils with high CEC might accumulate an excess of cations such as sodium (Na), particularly in regions already high in Na or where excessive Na addition occurs (9). This surplus could potentially lead to soil sodicity and create unfavorable physical conditions for plant growth.
Calcium, Mg, and K are essential cations that interact on soil exchange sites, influencing soil structure, fertility, and plant nutrition. The soil CEC, determined by clay and organic matter composition, serves as the battleground for these competitive interactions. Calcium, due to its smaller hydrated radius relative to Mg, tends to dominate exchange sites, forming robust bonds with negatively charged sites on clay and organic matter (10). This dominance influences soil structure and can limit the availability of other cations. Magnesium, an essential nutrient for plants, competes with Ca for exchange sites, resulting in calcium-magnesium interaction (11). Potassium, another critical plant nutrient, also competes for exchange sites with Ca and Mg (12), with Ca and Mg being preferentially adsorbed (13, 14). The intricate interplay of these cations on exchange sites has implications for nutrient uptake by plants, potentially leading to imbalances and affecting overall soil fertility. Imbalances in cation ratios may result in nutrient deficiencies, emphasizing the importance of understanding these competitive interactions for sustainable soil management and agricultural practices.
In addition to the intricate cation interactions, the incorporation of biochar into soils has emerged as a noteworthy factor influencing soil CEC. The porous structure and high surface area of biochar provide abundant binding sites for cations (15), contributing to increased CEC. This augmentation in CEC not only affects the retention and availability of essential nutrients but also influences the competitive dynamics among cations. Furthermore, the introduction of biochar can alter the soil’s physicochemical properties, influencing its overall fertility and promoting sustainable agricultural practices (16). As a result, understanding the interplay between traditional cations, such as Ca, Mg, and K, and the transformative impact of biochar on CEC is crucial for developing holistic strategies to optimize soil health and fertility.
This study aimed to investigate the influence of biochar on soil CEC. Our specific objectives were:
1. Investigate the influence of switchgrass-derived biochar (SGB) and poultry litter-derived biochar (PLB) on soil CEC through experiments without and with ryegrass cultivation, assessing five biochar application rates.
2. Evaluate the role of soil extractable calcium and magnesium/potassium ratio ([Ca+Mg]/K) concerning soil CEC for plant growth, aiming to establish optimal ryegrass production thresholds.
3. Develop predictive models for post-biochar application on soil CEC changes.
This comprehensive verification process ensures at which level biochar effectively enhances soil nutrient availability (while simultaneously binding and immobilizing contaminants as demonstrated in a previous study by 17). We hypothesized that (i) biochar application will alter soil CEC, (ii) the properties of the biochar, such as ash content, will play a critical role in influencing soil CEC dynamics, (iii) the calcium and magnesium/potassium ratio ([Ca+Mg]/K) will be of greater importance than CEC alone for ryegrass growth in biochar-amended soils, and (iv) predictive models for soil CEC changes post-biochar application can be developed relying on initial soil and biochar CEC.
https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/soil-science/articles/10.3389/fsoil.2024.1371777/full
Aluminium(3+) is an aluminium cation that has a charge of +3. It is an aluminium cation, a monoatomic trication and a monoatomic aluminium.
When considering the cation exchange capacity (CEC) of biochar and the ratio of calcium (Ca), magnesium (Mg), and potassium (K), a typical ideal ratio is often cited as Ca:Mg:K = 88:11:1; meaning that for optimal plant growth, the majority of the exchangeable cations on the biochar should be calcium, with smaller proportions of magnesium and potassium respectively.
Key points about CEC and biochar Ca:Mg:K ratio:
This ratio is significant because it affects nutrient availability for plants, with calcium playing a crucial role in cell wall structure and magnesium being important for chlorophyll synthesis, while potassium is involved in enzyme activation.
Impact of biochar type:
The exact optimal ratio can vary depending on the type of feedstock used to produce the biochar, as different biomass sources will have varying mineral compositions.
Soil analysis is key: To determine the best Ca:Mg:K ratio for your specific soil, it's important to conduct a soil test to analyze the existing cation balance.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0959652624009028
7 likes
comments
Share
6
Week 6. Vegetation1y ago
63.5 cm
Height
12 hrs
Light Schedule
26 °C
Day Air Temp
6.3
pH
600 PPM
TDS
60 %
Air Humidity
18 °C
Substrate Temp
21 °C
Night Air Temp
378.54 liters
Pot Size
88.9 cm
Lamp Distance
900 PPM
CO₂ Level
Nutrients 2

RAW Amino Acids
0.33 mll

RAW Enzymes
0.33 mll
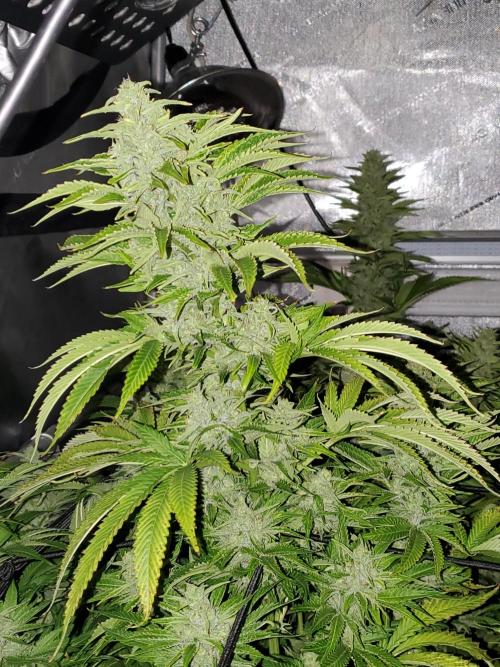
Ultraviolet Adjusting and fine-tuning her setup for the transition. Utilizing a double net this time and planning to oversate with red wavelengths for a week before making precise adjustments. Reduced light cycle to 12 hours and increased the PPFD. Now a matter of waiting. During the last grow, I was uncertain whether the delay in flowering was due to disruptions in the dark period, excessive sugar, or an overabundance of nitrogen. Initially, I couldn't the exact cause.
"High concentrations of sugar can delay flowering by prolonging the late vegetative phase. This postpones the activation of LFY expression, which governs floral transition. Sugar signals play a crucial role in all key transitions of plant life cycle and interact with hormone signaling pathways."
"Nitrogen (N) is one of the most abundant nutrients essential for plant growth and influences developmental regulation, including flowering. The effects of N on flowering regulation vary depending on its concentration, as both deficiency and excess of N lead to delayed flowering."
"Red light wavelengths, ranging between 600–700 nanometers (nm), interact with phytochromes to influence plant morphology, promoting budding and flowering. Red light impacts hormones such as auxins, which regulate plant elongation and flower development. Phytochromes are also involved in shade avoidance and detecting changes in the local light environment and seasonal timing."
UVA on with predominantly red light at sunrise (3000K),
UVB peak with blue light at noon (5000K),and a
UVA off with predominantly far-red light at sunset (3000K).
Also has a light coating of 850nm&940nm IR,
Approximately 45% of the sunlight reaching the Earth's surface is infrared (IR) light. Infra primarily provides heat to plants, which can promote growth a certain range; however, excessive IR can lead to stress, damage, or even in plants to overheating, disrupting photosynthetic processes. While plants do not directly use IR for photosynthesis, it can influence factors such as flowering and leaf expansion when present in appropriate. In particular far-red wavelengths can shade avoidance response, where plants detect a lack of direct light and growth to access better light conditions. This effect is especially beneficial in indoor environments where light conditions are carefully controlled. Increasing infrared light can impact the rate of plant stems, as short exposure to increases the between nodes. However, excessive infrared exposure can harm plants, type of light emits significant heat
Although the spectral composition sunlight sunrise and sunset is fundamentally similar the primary distinction lies in the enhanced scattering of shorter wavelengths, such as blue and violet light, during these periods. This phenomenon occurs due to the longer atmospheric path sunlight travers, leading a more vivid red and orange hue the horizon, as longer wavelengths scatter less and are more likely to reach our eyes. A sunset typically contains far-red light compared to a sunrise because the sunlight's path through the atmosphere is even longer at sunset, resulting in greater scattering of blue light and a higher proportion of red and far-red wavelengths becoming visible to the observer.
The Pr/Pfr ratio refers to the proportion of phytochrome Pr to phychrome Pfr in a. This ratio fluctuates throughout the day and night, influencing the plant's growth and flowering processes.
How does the ratio change?
Daytime: Red light converts Pr to Pfr, resulting in a low ratio.
Nighttime: Far-red light converts Pfr to Pr, resulting in a high ratio.
Seasons: The ratio varies with the seasons due to changes in day length and the sun's position.
How does the ratio affect plants?
Photomorphogenesis: The influences photomorphogenesis, the process by which a seed develops into a sprout.
Flowering: The ratio determines whether short-day or long-day plants flower.
Growth: The ratio impacts plant growth; for instance, a lower red to far-red light ratio can enhance growth under saline conditions.
How do plants sense the ratio?
Plants utilize pigments to detect the ratio of to far-red light, employing phytochrome system to measure this ratio during dawn and dusk. This plants regulate their growth in response seasonal changes.
In controlled environment agriculture, customized light treatments using light-emitting diodes are crucial to improving crop yield and quality. Red (R; 600-700 nm) and blue light (B; 400-500 nm) are two major parts of photosynthetically active radiation (PAR), often preferred in crop production. Far-red radiation (FR; 700-800 nm), although not part of PAR, can also affect photosynthesis and can have profound effects on a range of morphological and physiological processes. However, interactions between different red and blue light ratios (R:B) and FR on promoting yield and nutritionally relevant compounds in crops remain unknown. Here, lettuce was grown at 200 µmol m-2 s-1 PAR under three different R:B ratios: R:B87.5:12.5 (12.5% blue), R:B75:25 (25% blue), and R:B60:40 (40% blue) without FR. Each treatment was also performed with supplementary FR (50 µmol m-2 s-1; R:B87.5:12.5+FR, R:B75:25+FR, and R:B60:40+FR). White light with and without FR (W and W+FR) were used as control treatments comprising of 72.5% red, 19% green, and 8.5% blue light. Decreasing the R:B ratio from R:B87.5:12.5 to R:B60:40, there was a decrease in fresh weight (20%) and carbohydrate concentration (48% reduction in both sugars and starch), whereas pigment concentrations (anthocyanins, chlorophyll, and carotenoids), phenolic compounds, and various minerals all increased. These results contrasted the effects of FR supplementation in the growth spectra; when supplementing FR to different R:B backgrounds, we found a significant increase in plant fresh weight, dry weight, total soluble sugars, and starch. Additionally, FR decreased concentrations of anthocyanins, phenolic compounds, and various minerals. Although blue light and FR effects appear to directly contrast, blue and FR light did not have interactive effects together when considering plant growth, morphology, and nutritional content. Therefore, the individual benefits of increased blue light fraction and supplementary FR radiation can be combined and used cooperatively to produce crops of desired quality: adding FR increases growth and carbohydrate concentration while increasing the blue fraction increases nutritional value.
https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/plant-science/articles/10.3389/fpls.2024.1383100/full
Here are a few examples of good time lapse intervals based on the subject:
Fast-moving clouds, traffic: 1-2 seconds
Sunsets, sunrises, slower clouds: 2-5 seconds
Moving shadows, sun across the sky (no clouds): 15-30 seconds
Star trails: 30 seconds or longer
Plant growth, construction projects: Minutes or longer intervals
9 likes
comments
Share
7
Week 7. Flowering1y ago
83.82 cm
Height
12 hrs
Light Schedule
27 °C
Day Air Temp
6.7
pH
55 %
Air Humidity
21 °C
Substrate Temp
21 °C
Night Air Temp
378.54 liters
Pot Size
1100 PPM
CO₂ Level
Nutrients 7
Zeaxanthin
0.33 mll
Ascorbic Acid
0.33 mll
Agave Nectar
0.33 mll
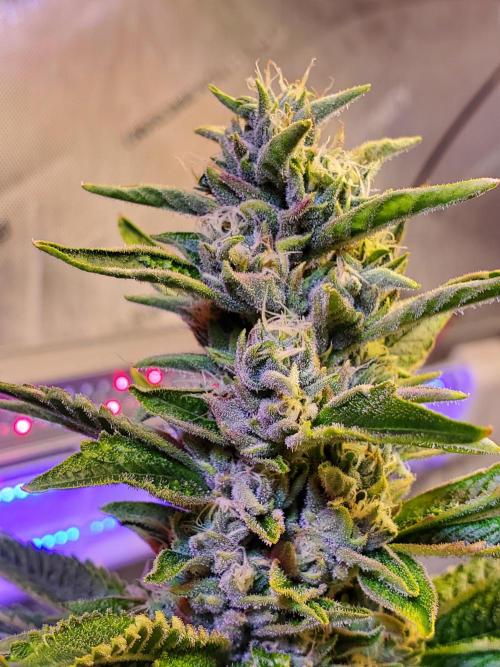
Ultraviolet Behind the logic. The keyword for the week is supersaturation. High-intensity interval stress training.
Photosynthetic efficiency is the fraction of light energy converted into chemical energy during photosynthesis in green plants and algae. The simplified chemical reaction can describe photosynthesis
6 H2O + 6 CO2 + energy → C6H12O6 + 6 O2
where C6H12O6 is glucose (which is subsequently transformed into other sugars, starches, cellulose, lignin, and so forth). The value of the photosynthetic efficiency is dependent on how light energy is defined – it depends on whether we count only the light that is absorbed, and on what kind of light is used (see Photosynthetically active radiation). It takes eight (or perhaps ten or more) photons to use one molecule of CO2. The Gibbs free energy for converting a mole of CO2 to glucose is 114 kcal, whereas eight moles of photons of wavelength 600 nm contains 381 kcal, giving a nominal efficiency of 30%. However, photosynthesis can occur with light up to wavelength 720 nm so long as there is also light at wavelengths below 680 nm to keep Photosystem II operating (see Chlorophyll). Using longer wavelengths means less light energy is needed for the same number of photons and therefore for the same amount of photosynthesis. For actual sunlight, where only 45% of the light is in the photosynthetically active wavelength range, the theoretical maximum efficiency of solar energy conversion is approximately 11%. In actuality, however, plants do not absorb all incoming sunlight (due to reflection, respiration requirements of photosynthesis, and the need for optimal solar radiation levels) and do not convert all harvested energy into biomass, which results in a maximum overall photosynthetic efficiency of 3 to 6% of total solar radiation. If photosynthesis is inefficient, excess light energy must be dissipated to avoid damaging the photosynthetic apparatus. Energy can be dissipated as heat NPQ (non-photochemical quenching) , or emitted as chlorophyll fluorescence.
4 Hours of 1000PPFD-1800PPFD @ UVB peak in the afternoon, 4 hours of 700-1000ppf on either side with differing ratios of PR/PRF and Peak UVA @ both Sunrise and Sunset, nature knows best.
34,560,000-54,720,000 µmol or 35-55 moles per day. Humidifier days, the relative humidity typically remains around 30-40 and the humidifier activates to maintain 65%, which is not difficult at 77°F as temperature adjustment of lights off handles the rest. Refill the humidifier once morning. If the humidity drops below 40%, it indicates that water levels are running low in the medium. The large, fluffy (CEC) salt mineral battery storage device needs to replenished and saturated. Check the EC and, low, increase PPM to reach the EC. Test the pH to assess the base saturation (BS).
The surface of a leaf is directly influenced by its transpiration. Higher rates of transpiration result in a cooler surface, as the evaporation of water absorbs heat energy, thereby cooling the leaf. Conversely, when transpiration rates are low, the leaf surface can become significantly warmer than the surrounding environment
Daytime VPD shows a -1°F to -5°F difference between ambient and LST, depending on level of transpiration. At night, VPD shows no difference (0°F), as there is no transpiration occurring. It is transpiration, not respiration, that cools surfaces through evaporative cooling, as the evaporation of water from the leaf surface energy, drawing heat away from the leaf and reducing its temperature.
CO2 fluctuations anywhere from 1400ppm from early morning to night around 600ppm with just compensation point. Reaching around 2500ppm peak when it's most efficient to do so.
14400 seconds in 4 hours, daylight@ 76F,60%RH, 700-1000ppfd UV-A 365nm 10080000-14400000µmol High Pr/Pfr ratio 3000k.
90%Transpiration 10% Respiration
14400 seconds in 4 hours, daylight@ 86F,50%RH 1000-1800ppfd UV-A 385nm+UV-B 285nm 14400000-25920000µmol 5000k+440nm co2 2000+ppm.
90%Transpiration 10% Respiration
14400 seconds in 4 hours, daylight@ 76F,60%RH 700-1000ppfd UV-A 365nm 10080000-14400000µmol High Pfr/Pr ratio 3000k.
90%Transpiration 10% Respiration
14400 seconds in 4 hours, night@ 70F, 45-50%RH.
100%Respiration = constant moisture production
14400 seconds in 4 hours, night@ 70F, 45-50%RH.
100%Respiration = constant moisture production
14400 seconds in 4 hours, night@ 70F, 45-50%RH.
100%Respiration = constant moisture production
Daytime negative pressure is maintained connecting the main to the humidifier, keeping the relative humidity ( at 60-65, ingredient humid set to 70, using approximately 3-4 liters. The constant cycling of passive exhaust fan creates optimal negative pressure to support plant growth. The tent is equipped with multiple exhausts: low C, inexpensive 8" fan RH, which vents into the room and is intentionally weaker to promote negative pressure while sufficient airflow to handle any fresh moisture vapor released the plants. The second exhaust is more powerful and directly linked outside, but it remains unused since cooling has been installed.
Nighttime negative pressure is simplified since the plant releases moisture throughout the night, without heat to cause evaporation. The relative humidity is set to 50-55% or adjusted as needed. As the plant grows, its water footprint expands, causing the fan to activate more frequently. Currently, the fan operates 75% of the time, maintaining consistent negative pressure within the tent. This serves as a reliable indicator of the plant's activity as it grows, with the fan gradually increasing its operation over time.
UVB levels 12W/m2 @ 14400 seconds, UVB Dose 172,800.00 J/m2
Of the global UV radiation at the ground, 94% is UV-A, 6% is UV-B.
Of the erythemal UV radiation, however, 17% is UV-A, 83% is UV-B at Solar noon.
The erythemal UV index -- usually simply called the UV index (UVI) -- is an estimation of the UV levels that are important for the effects on the human skin, where 1 unit equals 25 mW/m2. It is usually given for local solar noon when the Sun is highest in the sky, and it is valid for clear-sky conditions: effects of clouds shielding part of the UV radiation are not taken into account.
The erythemal UV index is an artificial quantity derived from the erythemal irradiance, which is an integration of the UV irradiance at the ground weighted by the CIE spectral action spectrum. The CIE action spectrum is a model for the susceptibility of the caucasian skin to sunburn (erythema). It is proposed by McKinlay & Diffey (1987) and adopted as a standard by the Commission Internationale de l'Éclairage (International Commission on Illumination).
Photolyase is a light-driven DNA repair enzyme that repairs UV-induced DNA damage, particularly cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers (CPDs), using blue light as an energy source, and is found in bacteria, fungi, plants, and some animals, but not in placental mammals. That's why we need 5000k at Solar noon. Cryptochromes are photoreceptor proteins, evolutionarily related to DNA photolyases, that regulate light-dependent processes in plants and animals, including circadian rhythms, photomorphogenesis, and UV-A/blue light responses.
Photolyases (EC 4.1.99.3) are DNA repair enzymes that repair damage caused by exposure to ultraviolet light.
https://www.mdpi.com/2075-1729/14/7/822
Mechanism:They directly reverse the damage, restoring the original pyrimidine bases.
Light Requirement:Photolyases require visible light (from the violet/blue end of the spectrum) for both their own activation and for the actual DNA repair process. Photolyases are found in many prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms, but not in mammals.
In just a few seconds, ultraviolet light from the sun can damage DNA by creating hundreds of unwanted links within DNA’s double helix. These modifications make the genetic material bulky and unreadable by DNA replication tools, leading to permanent mutations that can cause cancer and other diseases if left unrepaired.
But the same sunlight that carries damaging UV rays also contains blue light that can induce photolyase to quickly repair any DNA damage. Photolyase is thought to be one reason why plants – which have hours of exposure to the sun each day – are less susceptible to UV damage than humans, who lack photolyase. Humans and other mammals must fall back on alternative DNA repair mechanisms (or avoid going out into the sun altogether).
Vitamin D production in the skin is primarily stimulated by UVB radiation with wavelengths between 290 and 320 nanometers (nm). This specific range of UVB is crucial for the body to synthesize vitamin D from 7-dehydrocholesterol.
Humans are generally unable to see ultraviolet (UV) light due to the natural filtering effect of the eye's lens and cornea, which block most UV radiation from reaching the retina. However, under certain conditions, such as after cataract surgery where the lens is removed, some individuals report an ability to perceive UV light, often describing it as a whitish-blue or violet hue. This phenomenon occurs because the photoreceptor cells in the retina, particularly the short-wavelength cones, can detect UV light if it reaches them. While this capability is not typical for most people, it highlights the potential for human vision to extend beyond the conventional visible spectrum under specific circumstances.
Water vapor is extracted strictly 45-50% at night as a by-product of cellular respiration, providing almost constant negative pressure. As the plant grows, it increases in frequency as more water is moved, CO2 is dense and accumulates in the lower part of the tent with a vertical fan switched off at night. Plant gobbles this up in the morning, along with a well-earned baking soda and vinegar bomb for the afternoon UVB peak, along with 4 hours of song to help increase stomatal aperture.
Remain receptive,
•The level of antioxidants depends on the stress severity and duration.
•The plant’s antioxidants respond to light and temperature in a short- and long-term manner (acclimation).
•Under severe, short stress, the levels of antioxidants tend to decrease.
•Under acclimation (long-term responses) the levels of antioxidants gradually increase.
Cannabis contains antioxidants like cannabinoids, flavonoids, and phenolic compounds. Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) Has been shown to be an antioxidant and prevent hydroperoxide-induced oxidative damage.
Auxins are mainly involved in plant growth at the tips of plants. Gibberellins are involved in stem elongation, as well as various other aspects of plant growth such as flowering and fruit production. Abscisic acid (ABA) is the hormone that acts opposite to auxins, gibberellins, and cytokinins.
Abscisic acid is the plant hormone that controls the organ size and stomatal closure, and also actively responds against environmental stress or biotic stress. (RH drops below 20% stomata are forced closed by ABA, preventing the release of VOC through stomata)
Some plants release volatile organic compounds (VOCs) that can attract pollinators from a distance. Plants employ various mechanisms to attract pollinators, including offering rewards like nectar and pollen, using visual cues like bright colors and patterns, and employing scents to guide pollinators.
Sensimilla cultivation is a serious matter for the plant.
Many flowers have a distinct scent that attracts specific pollinators. For example, some flowers have a strong, sweet smell that attracts bees, while others have a more musky scent that attracts beetles. Plants interact with other organisms employing volatile organic compounds (VOCs). The largest group of plant-released VOCs are terpenes, comprised of isoprene, monoterpenes, and sesquiterpenes. Cannabis plants release volatile organic compounds (VOCs) through their stomata, which are tiny pores on the surface of leaves and other tissues, facilitating gas exchange and VOC emission.
In cannabis, terpene production is signaled by a combination of environmental factors, including light exposure (especially UV radiation), temperature fluctuations, and stress, as well as genetic factors and plant age, all of which influence the plant's defense mechanisms and terpene biosynthesis pathways. Jasmonic acid (JA) and its derivatives, collectively known as jasmonates, are crucial plant hormones that play a key role in modulating terpene accumulation, particularly in response to stress or defense signals.
Terpenes are aromatic compounds that give cannabis some of its most distinct aromas from citrus and berry, to more earthy tones. Many species of plants produce and emit terpenes in a diurnal, or daily cycle that is regulated by a complex web of signaling. There are also many plants that emit terpenes at night to attract nocturnal pollinators (Marinho et al., 2014346). Regardless of when the terpenes are produced or emitted, these processes are often dependent upon cues derived from natural light/dark cycles via a native circadian clock (Dudareva et al., 2004). Several light-sensitive pigments are involved in these processes of production and emission, and the different photoreceptors are dependent upon different wavelengths of light to be activated or deactivated. Emission of terpenes is a process that is entirely dependent upon phytochromes and red/far-red light cues in most plant species (Flores and Doskey, 2015). For example, repeated light/dark phytochrome signaling is necessary for the emission of terpenes in tobacco plants (Roeder et al., 2007). Based on previous findings, we hypothesized that a lack of red light and phytochrome-mediated light/dark signaling on the part of the plant is responsible for an increase in terpene content in cannabis. The plant continues to synthesize terpenes, but a lack of red light to trigger the Pr-Pfr shift results in a lack of terpene emission by the plant, thus causing the terpenes to accumulate in the maturing flowers.
REFERENCES
Dudareva N, Pichersky E, Gershenzon J. Biochemistry of Plant Volatiles. Plant Physiology. 2004;135(4):1893-1902. Flores, R.M., Doskey, P.V., Estimating Terpene and Terpenoid Emissions from Conifer Oleoresin Composition. Atmospheric Environment. 2015. 113, 32-40. Marinho, C.R.; Souza, C.D.; Barros, T.C.; Teixeira, S.P.; Dafni, A. Scent glands in legume flowers. Plant Biology , Volume 16 (1) – Jan 1, 2014 Roeder S, Hartmann AM, Effmert U, Piechulla B (2007) Regulation of simultaneous synthesis of floral scent terpenoids by the 1,8-cineole synthase of Nicotiana suaveolens. Plant Mol Biol 65: 107-12
UV Radiation: Studies suggest that UV-B radiation can increase trichome numbers and terpene content.
Light Stress: Light stress, potentially from intense or prolonged exposure, can trigger terpene production as a defense mechanism.
LED Lighting: Different light spectra, including supplemental green light, can influence terpene and THC accumulation, but not CBD.
Temperature Fluctuations: Dropping temperatures during the last week of flowering can enhance terpene production.
General Stress: Plants under stress, whether from light, temperature, or other factors, may produce more terpenes as a defense mechanism.
Stress, stress, stress, stress, transpirational stress, salinity stress, drought stress, training stress, wind stress, light stress, stressing me out man! Only through great stress does growth occur. Some like to make subtle comments that my tips are burnt, or maybe my VPD is a little too high. Thats kinda the point.
Plants are an integral component in the global movement of water from the soil to the atmosphere, which is referred to as the hydraulic soil–plant–air continuum. Gradients of water vapor generate strong forces for water mobilization. At 20 °C, for example, a one percent difference in water saturation between plant tissues and the air generates a water potential difference of −1.35 MPa (−13.5 bar) which drives transpiration. In essence, plants facilitate the translocation of water from the root zone, back into the air.
A number of different endogenous signals have been proposed for long-distance communication of the water deficit of roots to leaves. These range from chemical to hydraulic, and electric signals. ABA was identified as a chemical being delivered in increased amounts to the shoot in the transpiration stream during drought. Electrical signals emanate from water-stressed roots or from roots after re-irrigation and have been suggested to be relayed independently of hydraulic function.
How is the change in Ψw sensed within the plant? The hydraulic signal generated by water deficit causes first, a reduction of turgor and second, a moderate increase in solute concentrations because of water withdrawal from cells, and third, mechanical forces exerted at the cell wall and at the cell wall-plasma membrane interface. Pioneering work uncovered the importance of turgor loss for triggering ABA biosynthesis whereas lowering cellular osmotic potential without reducing turgor was noted.
Plants have evolved several efficient protective mechanisms that make it possible for them to survive under unfavorable light and temperature conditions. These mechanisms are linked predominantly to the photosynthetic electron transport chain, the xanthophyll cycle, and the photorespiratory pathway. Under stress conditions, elevated levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS) are produced, which in addition to deleterious effects also show signaling functions. In response to enhanced ROS formation, different low-molecular antioxidants are synthesized, as well as antioxidant enzymes. Depending on the stress intensity and its duration, the content of synthesized antioxidants varies. Under severe, short light/temperature stress, the contents of low-molecular-weight antioxidants, such as ascorbate, glutathione and prenyllipids, tend to decrease, which is correlated with an extra need for ROS scavenging. Under longer exposure of plants to unfavorable light and temperature conditions, the contents of antioxidants gradually increase as a result of acclimation during long-term responses. Studies on plant antioxidant responses indicate that a crucial part of the antioxidant network operates in chloroplasts and their action shows a high level of interdependence. The antioxidant response also depends on plant stress tolerance.
Under acclimation (long-term responses) the levels of antioxidants gradually increase.
Ascorbic acid and Zeanathaxin are the two co-enzymes responsible for ROS and NPQ, helping the plant deal with the rigors of excess light.
Too much light can be harmful and excess light energy can be dissipated as fluorescence or heat (nonphotochemical quenching, NPQ). At least part of this nonradiative energy dissipation occurs through reversible covalent modifications of the thylakoid xanthophylls and involves the reductive de-epoxidation of violaxanthin to zeaxanthin (xanthophyll cycle) that is triggered by the pH gradient produced by photosynthetic electron flow. A genetic analysis of NPQ-deficient mutants provided direct genetic evidence for the importance of zeaxanthin in NPQ and also revealed that the pigments of the xanthophyll cycle derived from β-carotene, and lutein derived from α-carotene are required both for NPQ and for protection against oxidative damage in high light.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/medicine-and-dentistry/xanthophyll-cycle
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0098847217301065?via%3Dihub
Induction of metabolite biosynthesis and accumulation is one of the most prominent UV-mediated changes in plants, whether during eustress (positive response) or distress (negative response). However, despite evidence suggesting multiple linkages between UV exposure and carotenoid induction in plants, there is no consensus in the literature concerning the direction and/or amplitude of these effects.
it was found that violaxanthin was the only carotenoid compound that was significantly and consistently induced as a result of UV exposure. Violaxanthin accumulation was accompanied by a UV dose dependent decrease in antheraxanthin and zeaxanthin. The resulting shift in the state of the xanthophyll cycle would normally occur when plants are exposed to low light and this is associated with increased susceptibility to photoinhibition. Although UV induced violaxanthin accumulation is positively linked to the daily UV dose, the current dataset is too small to establish a link with plant stress.
protection of polyunsaturated lipids by zeaxanthin is enhanced when lutein is also present. During photooxidative stress, α-tocopherol noticeably decreased in ch1 npq1 and increased in ch1 npq2 relative to ch1, suggesting protection of vitamin E by high zeaxanthin levels. Our results indicate that the antioxidant activity of zeaxanthin, distinct from NPQ, can occur in the absence of PSII light-harvesting complexes. The capacity of zeaxanthin to protect thylakoid membrane lipids is comparable to that of vitamin E but noticeably higher than that of all other xanthophylls.
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC2151694/
Lutein and Zeaxanthin: These powerful antioxidants are found in the retina and help protect your eyes from harmful blue light and oxidative .
https://clinmedjournals.org/articles/ijocr/international-journal-of-ophthalmology-and-clinical-research-ijocr-2-044.php?jid=ijocr
In an in vitro model, L/Zi treatment inhibited cholinesterase activity and enhanced catalase activity. These results suggest that inhibition of cholinesterase enzyme and enhancing antioxidant enzymes activities may have several therapeutic applications such as neurodegeneration disorders and myasthenia gravis. Mild UV irradiation affected significant changes in 545 genes, including down-regulation of c-SRC and β-catenin, and up-regulation of VEGF and FOXO-3A. L/Zi induced changes in 520 genes, most notably down-regulation of β-catenin, and up-regulation of specific G-protein constituents that support neurophysiologic processes in vision and enhanced immune system poise. L/Zi supplemented cells were mild UV irradiated, 573 genes were significantly affected, most notably an up-regulation of c-SRC. There were changes in cytokine gene expression and enhancement in SOD and GPx activities.
Conclusions: L/Zi treated cells may ameliorate the effects of mild UV irradiation on RPE cells, as shown by the expression of genes involved in cell proliferation, inflammation, immune function and wound healing.
https://clinmedjournals.org/articles/ijocr/international-journal-of-ophthalmology-and-clinical-research-ijocr-2-044.php?jid=ijocr
Zeaxanthin is a predominant xanthophyll in human eyes and may reduce the risk of cataracts and age-related macular degeneration. Spirulina is an algal food that contains a high concentration of zeaxanthin.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0981942822002121
When a plant is exposed to UV-A radiation, it can lead to a decrease in zeaxanthin levels due to the activation of the xanthophyll cycle, which typically converts zeaxanthin back to violaxanthin as a protective mechanism against high light conditions, including UV radiation; essentially, the plant may use up its zeaxanthin to protect itself from potential damage caused by the UV-A exposure.
Key points about UV-A and zeaxanthin in plants:
Xanthophyll cycle:
Plants use a cycle involving pigments like zeaxanthin and violaxanthin to adjust to changing light conditions. When exposed to high light (including UV), the plant converts zeaxanthin back to violaxanthin to protect the photosynthetic apparatus.
UV-B and UV-A radiation are natural components of solar radiation that can cause plant stress, as well as induce a range of acclimatory responses mediated by photoreceptors. UV-mediated accumulation of flavonoids and glucosinolates is well documented, but much less is known about UV effects on carotenoid content. Carotenoids are involved in a range of plant physiological processes, including photoprotection of the photosynthetic machinery. UV-induced changes in carotenoid profile were quantified in plants (Arabidopsis thaliana) exposed for up to ten days to supplemental UV radiation under growth chamber conditions. UV induces specific changes in carotenoid profile, including increases in antheraxanthin, neoxanthin, violaxanthin, and lutein contents in leaves. The extent of induction was dependent on exposure duration. No individual UV-B (UVR8) or UV-A (Cryptochrome or Phototropin) photoreceptor was found to mediate this induction. Remarkably, UV-induced accumulation of violaxanthin could not be linked to the protection of the photosynthetic machinery from UV damage, questioning the functional relevance of this UV response. Here, it is argued that plants exploit UV radiation as a proxy for other stressors. Thus, it is speculated that the function of UV-induced alterations in carotenoid profile is not UV protection, but rather protection against other environmental stressors such as high-intensity visible light that will normally
accompany UV radiation.
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/366352446_UV_Radiation_Induces_Specific_Changes_in_the_Carotenoid_Profile_of_Arabidopsis_thaliana
11 likes
comments
Share
8
Week 8. Flowering1y ago
101.6 cm
Height
12 hrs
Light Schedule
27 °C
Day Air Temp
6.5
pH
55 %
Air Humidity
21 °C
Substrate Temp
21 °C
Night Air Temp
378.54 liters
Pot Size
1500 PPM
CO₂ Level
Nutrients 11
Agave Nectar
5.21 mll
Monopotassium Phosphate
7.81 mll
Honey
0.65 mll
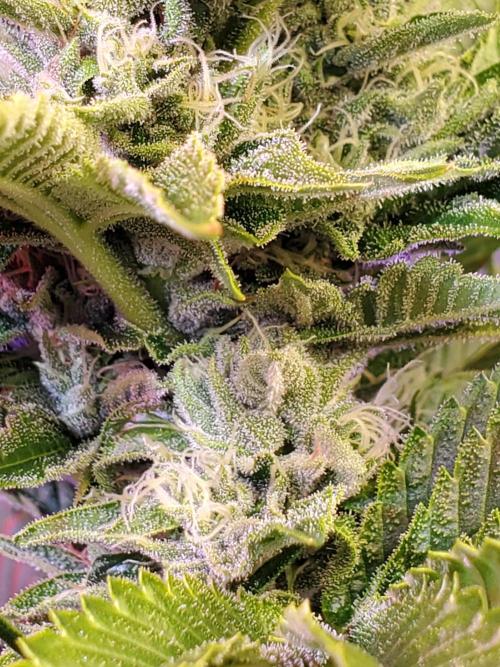
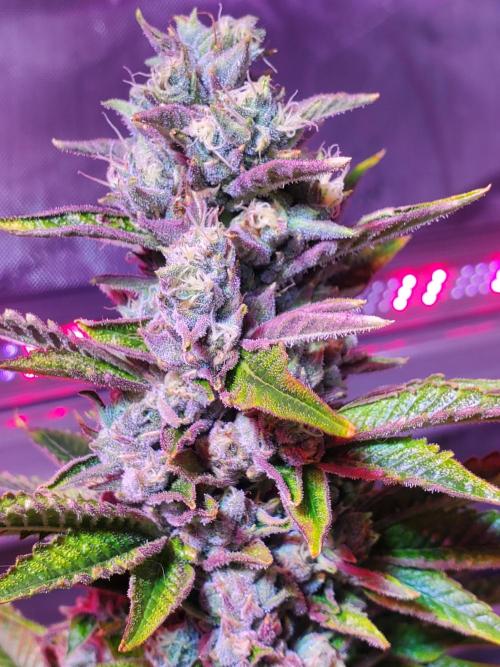
Ultraviolet Buds have tiny little trichomes already. 😮Not the good kind of course, but still.
Magnesium is the central atom in the chlorophyll molecule. Nitrogen forms the ring around the core. The presence of magnesium in chlorophyll is what gives plants their green color. While nitrogen is also important for plant growth, it is not directly responsible for chlorophyll's green color; it is a component of the chlorophyll molecule but not the central atom.
The resonant frequency of pure magnesium is 4,620 Hz, If a guitar string is plucked and we hear a sound, it is not too difficult for the human mind to associate this sound with the vibration of the guitar string. With color, it is quite different. It is difficult for us to conceive that the color of a substance is not an inherent property of the substance itself, but an indication picked up by our senses of that substance's ability to absorb or reflect the light which happens to be shining on it at that moment. Neither the matter nor the light is colored. What happens is that the brain learns to differentiate between the frequencies reflected or transmitted by the substance the eyes are focused on. The same thing happens with sound.
When discussing the "frequency" of magnesium in terms of light, it refers to the wavelength of light emitted or absorbed by magnesium atoms, which is primarily around 285.2nm UV-B.
Key points about magnesium and its wavelength:
Absorption wavelength:
A dodecahedron is a 3D shape with 12 faces, and while not all dodecahedra are regular, the regular dodecahedron, a Platonic solid, can be formed by holmium-magnesium-zinc (Ho-Mg-Zn) quasicrystals.
Magnesium's role in the skin involves processes like tissue repair and suppression of inflammation.
Magnesium absorption in plants, vital for chlorophyll and photosynthesis, is influenced by soil conditions and can be affected by environmental factors like UV radiation, with magnesium also playing a role in plant resilience to stress.
Magnesium's Role:
Magnesium (Mg) is an essential macronutrient for plants, involved in various physiological and biochemical processes. It's a central component of chlorophyll, the pigment that absorbs sunlight for photosynthesis. Mg also plays a role in enzyme activation, nutrient metabolism, and cell membrane stability. Magnesium deficiency can lead to lower plant productivity and yield.
UV Radiation and Magnesium:
While the direct interaction between UV radiation and magnesium absorption is not well-elucidated, research suggests that magnesium plays a role in plant resilience against UV stress.
UVB radiation can induce cell damage, but MgCl2 supplementation can help alleviate UVB-induced cell damage.
Mg can also help plants withstand other environmental stressors like cold stress, improving photosynthetic activity and nutrient uptake.
Absorption Mechanisms:
Plants absorb magnesium in the form of Mg2+ ions from the soil.
Root health and function are crucial for magnesium uptake.
Factors like soil pH, nutrient availability, and environmental conditions can impact magnesium absorption.
10 likes
comments
Share
9
Week 9. Flowering1y ago
111.76 cm
Height
12 hrs
Light Schedule
27 °C
Day Air Temp
6.2
pH
500 PPM
TDS
55 %
Air Humidity
21 °C
Substrate Temp
21 °C
Night Air Temp
378.54 liters
Pot Size
2000 PPM
CO₂ Level
Nutrients 4
Potassium Sulfate
2.642 mll

Microbes Bloom Stage
0.65 mll

RAW Enzymes
0.65 mll
Ultraviolet Blue light bends more than red light because blue light has a shorter wavelength, causing it to be refracted more when passing through a medium like a prism, resulting in a greater bend compared to red light which has a longer wavelength. The human eye is a refractive medium that uses light-bending structures to focus images onto the retina. These structures include the cornea, lens, aqueous humor, and vitreous humor.
0:0:50 Potassium Sulphate
Sulfur is required for the synthesis of IPP and its conversion into other terpene compounds. Adequate sulfur availability ensures a sufficient supply of IPP, which can lead to increased terpene production. Activation of Enzymes: Sulfur is involved in the activation of enzymes responsible for terpene biosynthesis. Isopentenyl diphosphate (IPP) is a building block of terpenes, which are found in cannabis flowers. IPP is produced by the mevalonate (MVA) and methylerythritol phosphate (MEP) pathways. The mevalonate (MVA) and methylerythritol phosphate (MEP) pathways are both biosynthetic pathways that produce isoprenoids. Isoprenoids are the building blocks of many important compounds, including sterols, carotenoids, and vitamin E. To optimize the mevalonate (MVA) and methylerythritol phosphate (MEP) pathways, key strategies include: overexpressing key enzymes in each pathway, fine-tuning the expression levels to balance flux, utilizing metabolic engineering techniques to redirect precursor flow, and optimizing growth conditions to maximize production of desired isoprenoid products; considering the specific organism and target molecule, with a focus on the rate-limiting steps in each pathway and potential bottlenecks arising from the interaction between the two pathways. MVA pathway: Enzymes like HMG-CoA reductase (HMGR) and phosphomevalonate decarboxylase (PMD) are often considered rate-limiting. MEP pathway: Deoxyxylulose 5-phosphate synthase (DXS) is typically the primary control point in the MEP pathway. The key enzymes in the mevalonate (MVA) and methylerythritol phosphate (MEP) pathways are 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase (HMGR) and 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate synthase (DXS), respectively. The 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme-A (HMG-CoA) reductase (HMGR) enzyme is found in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) of eukaryotes. In prokaryotes, HMGR is soluble and found in the cytoplasm. HMGR: The rate-limiting enzyme in the MVA pathway. In prokaryotes, HMGR is soluble and found in the cytoplasm. Prokaryotes are organisms whose cells lack a nucleus and other organelles. Prokaryotes are divided into two distinct groups: the bacteria and the archaea, which scientists believe have unique evolutionary lineages. Most prokaryotes are small, single-celled organisms that have a relatively simple structure. The root zone harbors various species of beneficial bacteria, including Bacillus, Pseudomonas, and many others, that establish symbiotic relationships with cannabis roots.
https://bmcgenomics.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12864-021-07448-x
In cannabis cultivation, stomata typically begin to close when relative humidity (RH) reaches around 80% or higher; this is because high humidity limits the plant's ability to transpire water effectively, causing the stomata to close as a protective mechanism to prevent excessive water loss.
While RH is important, the most crucial factor is the "Vapor Pressure Deficit" (VPD), which considers both temperature and humidity. When VPD becomes too low (due to very high RH), stomata will close.
"VPD" stands for Vapor Pressure Deficit, which is a measure of how much moisture the air can still hold at a given temperature, while "absolute RH" refers to the actual amount of moisture in the air (absolute humidity), and "relative RH" is the percentage of moisture the air is holding compared to its maximum capacity at that temperature, meaning a higher VPD indicates drier air, even if the relative humidity remains the same, as the air can still hold more moisture; essentially, VPD is a more accurate measure of how readily water can evaporate from a surface compared to just relative humidity alone.
"Absolute humidity" refers to the actual amount of water vapor present in the air, measured in grams per cubic meter, while "relative humidity" is a percentage that indicates how much moisture is in the air compared to the maximum amount it can hold at a given temperature, essentially a ratio of the actual moisture to the maximum possible moisture at that temperature; meaning absolute humidity is a fixed value regardless of temperature, while relative humidity changes with temperature fluctuations.
Absolute humidity: Measures the actual amount of water vapor in the air. Expressed in units like grams per cubic meter. Does not change with temperature.
Relative humidity: Represents the percentage of water vapor in the air compared to its maximum capacity at a given temperature. Expressed as a percentage. Changes with temperature, even if the absolute humidity remains the same.
Example: Imagine a room with a certain amount of water vapor in the air (absolute humidity). If the temperature increases, the relative humidity will decrease because the air can now hold more moisture at the higher temperature, even though the absolute humidity stays the same.
Daycycle: At 30°C/86F, a leaf may transpire three times as fast as it does at 20°C/68F. Through stomata.
This is where the surface temperature of the leaves can make a difference, as the optimal temperature for the photosynthesis process is a stable 28˚C or 82.4˚F. Usually, the leaves are between 3° and 5° F cooler than the room because they are transpiring. The evaporation on the leaf's surface literally draws heat from the leaf, thereby cooling it. Endothermic.
Water cycling through plants is a process that involves water moving from the soil through the plant and back to the atmosphere through transpiration. This process is part of the larger water cycle. Water cycling and nutrient uptake are related because water dissolves nutrients and transports them to plants. However, the rate of nutrient uptake is not directly dependent on the rate of water uptake. Other factors that affect nutrient cycling include: Temperature, Salinity, and The atomic form of the nutrient. Ideally, you should aim to have your nutrient solution or irrigation water temperature at around 18 – 22 °C (65 - 72 °F) to ensure optimal nutrient and water uptake. In addition to having an effect on nutrient absorption, your root zone temperature also affects oxygen availability and solubility. Maintaining a stable root zone temperature within the optimal range is crucial for consistent nutrient absorption and healthy plant growth.
Nightcycle: Water vapor is a by-product of respiration, meaning it is produced as a result of the process of cellular respiration in plants when organisms breathe, they release water vapor alongside carbon dioxide as a waste product of exhalation through the stomata. Plants need oxygen at night not CO2, My fan is on almost all night just gently pushing out moisture, holding a strict 45-50%, this over time gives an indicator of how much work is being done by the plant, how much CO2 is being mixed with the energy harvested from daylight to create the excess moisture, once the plant fills a canopy, as soon as those lights go off and respiration begins, you better have your passive fan on along with exhaust ready to extract. The only time RH ever drops below 40% RH is when it's time to water. As soon as she starts to droop, its indicator turgor pressure is being lost. The cohesion-tension theory explains how negative pressure enables water movement from the roots to the leaves of a cannabis plant. As water evaporates from the leaf surfaces through stomata, tension is created, generating a suction force that pulls water upwards through the xylem vessels. This process relies on the cohesive forces between water molecules, forming a continuous column for efficient water transport. Water is one of the most important factors of cannabis growth and development; both transpiration and respiration involve water. Irregular watering can lead to irregular plant growth and development. Too little water and your plant can become dry, brittle, and stressed. Too much water and your plant’s roots can be deprived of important oxygen, and even drown. One of water’s most important purposes is the transportation and movement of nutrients and minerals, which are typically absorbed in the roots and distributed throughout the rest of the plant. The faster the plant can rid itself of water through transpiration, the faster it can uptake more water to get more nutrients to where they need to be, by creating a negative pressure we optimize the transpiration rate and maximize stomatal conductance, with sound frequency we open them further @noon for no more than 4 hours. Important, tranpiration gets its water from roots up the plant and out the stomata, respiration doesn't use water from root system, respiration water comes from the chemical reaction of cellular respiration(Nightcycle), where oxygen combines with hydrogen ions (produced during the breakdown of glucose) within the mitochondria of cells, forming water as a byproduct, specifically during the final stage called the electron transport chain; this water is then released through exhalation. Plant respiration is highly dependent on the moisture content in the soil, as the availability of water significantly impacts the activity of soil microbes which are responsible for decomposing organic matter and releasing carbon dioxide as a byproduct of their respiration, leading to a direct correlation between soil moisture and overall plant respiration rates; essentially, drier soil results in lower respiration rates due to reduced microbial activity, while excessively wet soil can also limit respiration by restricting oxygen availability to the microbes. This is why it can be beneficial to have your waterings in the morning. Takes time to make the medium just optimal for respiration to occur.
At night, plants primarily utilize active nutrient uptake mechanisms to absorb nutrients from the soil. This process is driven by the plant's metabolic energy and is less dependent on water uptake than daytime processes. While water uptake via osmosis may still occur, the main mechanism for nutrient absorption at night is an active transport system that moves ions against their concentration gradient, requiring energy from the plant. While stomata are generally closed at night to minimize water loss, they may still open slightly, especially if the plant needs to absorb nutrients. This minimal transpiration, combined with root pressure and foliar uptake, can still allow for some nutrient uptake during the night. In summary, while transpiration is the main driver of nutrient uptake during the day, plants also have mechanisms for nutrient uptake at night, including root pressure and foliar absorption, even with reduced transpiration.
Plants use phosphorus at night. While nutrient uptake may be higher during the day due to increased photosynthesis and transpiration, studies show that a significant portion of nutrient uptake, including phosphorus, can occur during the night. In fact, some studies indicate that nighttime nutrient uptake can be as high as 51% of the total uptake, especially in the early hours of the night. Phosphorus binds to several elements in the soil, making it less available for plant uptake, depending on the soil pH. At low pH levels (below 5.5), phosphorus binds to iron and aluminum. At high pH levels (above 7), it binds to calcium. The optimal pH range for phosphorus availability is between 6.0 and 7.0. Phosphorus uptake by plants is affected by oxygen availability in the soil. While not directly requiring oxygen to be absorbed, phosphorus availability and root function, which are crucial for uptake, are influenced by soil aeration. Phosphorus readily binds with oxygen in the environment, primarily forming phosphates, which are then the form plants readily uptake. This is crucial.
Optimal moisture level: Most soil microbes function best at intermediate moisture levels, where there is enough water for biochemical reactions without completely displacing air and limiting oxygen access.
Dry soil impact: When soil is too dry, microbial activity is significantly reduced, leading to a decrease in respiration and nutrient availability for plants.
Waterlogged soil impact: Conversely, waterlogged soil with very high moisture content can also hinder respiration by limiting oxygen availability to microbes, potentially leading to anaerobic conditions and the production of harmful byproducts like methane.
Water, water, water until? EC tells you to. A low soil EC reading indicates that it's likely time to fertilize, as a low EC signifies a low concentration of soluble salts and nutrients in the soil, meaning the plants may be lacking essential nutrients; conversely, a high EC reading suggests the soil is already sufficiently fertilized or even over-fertilized, potentially causing plant stress.
Ideal EC levels need to be adjusted as cannabis plants grow, typically starting at about 0.8-1.3 for seedlings and steadily increasing to about 1.5-2.0 during flowering. This will vary somewhat according to your chosen strain, your growing medium, the nutrient solution, and growing environment. EC levels that remain too low or too high can kill a plant. Thankfully, these levels can be adjusted to bring cannabis plants back to health if issues are identified quickly.
The key difference between "soil EC" (electrical conductivity of soil) and "water EC" is that soil EC measures the conductivity of the entire soil matrix, including both the solid particles and the water within the pore spaces, while water EC only measures the conductivity of the water itself; essentially, soil EC reflects the total salt content in the soil, whereas water EC represents the dissolved salts only in the water portion of the soil.
Electrical conductivity (EC) to parts per million (PPM) can be converted using a variety of formulas, including EC x 500 or EC x 700. The conversion factor used depends on the scale and the type of solution being measured.
Conversion formulas
EC x 500: Used to calculate PPM 500 or TDS
EC x 700: Used to calculate PPM 700
EC x 0.55: Used to get an approximate PPM equivalent
EC x 1000 / 2: Used to get an approximate sodium chloride TDS value
PPM x 2 / 1000: Used to get an EC value
Deeper.
A higher Pfr level (lower Pr:Pfr ratio) generally leads to increased plant growth and carbohydrate production.
When the "Pr:Pfr ratio is relatively large," it means that there is a higher concentration of the "Pr" form of phytochrome compared to the "Pfr" form, indicating that the plant is likely experiencing conditions with less red light and more far-red light, often signifying a shaded environment and potentially triggering responses like stem elongation to reach more light.
The Pfr form is generally considered the active form, meaning it triggers physiological responses in the plant when present in higher quantities.
Pr and Pfr are two forms of phytochrome, a light-absorbing protein that regulates physiological responses in plants. Photosystems I and II (PSI and PSII) are protein complexes that absorb light and transfer energy and electrons during photosynthesis.
Pr absorbs red light and Pfr absorbs far-red light
Pr and Pfr are reversible, meaning they can change back and forth depending on the light conditions.
Pfr is generally considered the biologically active form.
Photosystems I and II
PSI and PSII are found in the chloroplasts of plants and algae.
PSI absorbs far-red light and PSII absorbs red light.
PSI and PSII are involved in the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis.
Each photosystem has a reaction center and an antenna complex.
Phytochromes are found in plants, fungi, slime molds, bacteria, and heterokonts. They regulate a wide range of physiological responses, including seed germination, photomorphogenesis, and chloroplast movement.
The ratio of Pr to Pfr is one of the ways that a plant senses the quality and quantity of light it receives. The ratio of Pr to Pfr also affects when and how a plant flowers.
The Pr/Pfr ratio is the balance of phytochrome Pr and Pfr in a plant, which changes throughout the day and night. The ratio is affected by the amount of red and far red light the plant receives.
How does the ratio change?
Day: Red light converts Pr to Pfr, and the ratio decreases.
Night: Far red light converts Pfr to Pr, and the ratio increases.
What does the ratio indicate?
Daytime: A low ratio of Pr to Pfr indicates that the plant is receiving more red light than far red light.
Nighttime: A high ratio of Pr to Pfr indicates that the plant is receiving more far-red light than red light.
"Pr Pfr sugar signal" refers to the way that a plant's phytochrome protein, which exists in two forms - Pr (inactive, red light absorbing) and Pfr (active, far-red light absorbing), acts as a sensor for light conditions and subsequently influences the plant's sugar levels by regulating gene expression related to photosynthesis and carbohydrate metabolism, essentially acting as a "sugar signal" based on the light environment it experiences.
Gene regulation: The activated Pfr form can influence the expression of genes involved in photosynthesis, starch synthesis, and sugar transport, depending on the Impact on sugar levels: By regulating these genes, the plant can adjust its sugar production and allocation based on the amount of red light available.
Seed germination: When a seed is exposed to red light, the Pr to Pfr conversion activates genes responsible for amylase production, which breaks down starch into sugars needed for germination. Upon exposure to light, Pr is converted to Pfr, and Pfr signaling causes transcription of the gene that encodes amylase—an enzyme that breaks down starches stored in the seed into simple sugars. At this point, germination proceeds.
Pr and Pfr: The ratio of Pr to Pfr in a plant tells it how long the night is, which helps determine when to flower.
Pfr: The active form of phytochrome that can stimulate flowering in long-day plants. In short-day plants, Pfr can inhibit flowering.
Glucose, sucrose, and trehalose-6-phosphate (T6P): These sugars help control the expression of genes that regulate floral signal transduction.
Sugar accumulation: The spatial and temporal regulation of sugar accumulation is important in meristematic tissues.
Sugar distribution: The distribution of sugars directs plant development.
Other factors outside the photoperiod that influence flowering include: The concentration of carbohydrates and their relative ratios to other metabolites. The flux through sugar-specific transporters and/or sensors
A higher "Pr:Pfr" ratio generally indicates lower carbohydrate levels in a plant, as the "Pfr" form of phytochrome, which is activated by red light, is the active form that promotes plant growth and carbohydrate production, meaning a lower Pfr level (due to a higher Pr ratio) would result in reduced carbohydrate synthesis.
Key points about Pr:Pfr and carbohydrates: Phytochrome function: Phytochrome exists in two forms: Pr (inactive) and Pfr (active).
Light influence: Red light converts Pr to Pfr, while far-red light converts Pfr back to Pr.
Growth regulation: A higher Pfr level (lower Pr:Pfr ratio) generally leads to increased plant growth and carbohydrate production.
How it relates to plant environment:Shade avoidance: When a plant is in shade, the red light is filtered out, leading to a higher Pr:Pfr ratio, causing the plant to elongate its stems to reach more light.
Flowering: The Pr:Pfr ratio can also influence flowering time in plants depending on the day length and light quality.
https://medcraveonline.com/APAR/plant-responses-to-extended-photosynthetically-active-radiation-epar.html
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0005272818300367https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0005272818300367
1.1 – Photosynthetically active radiation (400-700nm), is that all plants care about?
McCree demonstrated that for a wide variety of plants grown outside and in growth chambers, radiation from 400-700nm (visible light) drove CO 2
https://biochambers.com/pdfs/far_red.pdf
https://opentextbc.ca/biology/chapter/5-2-the-light-dependent-reactions-of-photosynthesis/
Applied knowledge is the key, if you want her sugary!
9 likes
comments
Share
10
Week 10. Flowering1y ago
127 cm
Height
12 hrs
Light Schedule
27 °C
Day Air Temp
6.7
pH
650 PPM
TDS
55 %
Air Humidity
21 °C
Substrate Temp
21 °C
Night Air Temp
378.54 liters
Pot Size
1500 PPM
CO₂ Level
Nutrients 4

Bud Factor X
1.321 mll

RAW Cane Molasses
5.21 mll

RAW Calcium / Mag
0.65 mll
Ultraviolet Ok, so what does CRI have to do with grow lighting? To consider this we need to first review what color rendering index or CRI is. Put simply it’s a performance metric or outcome that considers the ability of a light source to mimic sunlight, 100 cri is sunlight at midday, so approximately 5000 kelvins on a clear sunny day. So, if we know that perfect light that is 100cri is perfect for replicating true color for say photographic applications where subjects perfectly lit will reveal perfect color, then why as a metric is it important for use in grow lights? The fundamentals of light that mimics sunlight are referred to in the grow light community as wide or broad-spectrum light. That is to say, all the wavelengths of sunlight at 100 CRI would be perfectly represented and would therefore provide a light that is sunlight, artificially produced. Ok so is CRI the nirvana of plant performance? Not quite. Let’s consider missing ingredients.
OK so measurement devices used for CRI are typically based around what is referred to as PAR. PAR stands for Photosynthetically Active Radiation. and it refers to the portion of the light spectrum (wavelengths) that plants use for photosynthesis. Specifically, it covers wavelengths between 400 and 700 nanometers (nm), which is the range most beneficial for plant growth.
While PAR (Photosynthetically Active Radiation) focuses on the 400–700 nanometer (nm) range of the light spectrum, it does however not cover all wavelengths that might influence plant growth.
Here’s what PAR leaves out when considering a full-spectrum light source for grow lighting:
UV-A (315–400 nm), UV-B (280–315 nm), and UV-C (280 nm).
Benefits to Plants: UV-A and UV-B can stimulate secondary metabolite production (e.g., flavonoids, anthocyanins, and terpenes), enhancing plant color, flavor, and pest resistance.
Far-Red Light –Light in the 700–800 nm range.
Benefits to Plants: Stimulates the shade-avoidance response, helping plants grow taller or stretch toward light.
Enhances flowering and fruiting when combined with red light in the Emerson Effect (synergy between red and far-red light to increase photosynthetic efficiency).
Limitations: Too much far-red can lead to elongated, weak plants with reduced yield. It’s a balancing act
UV-B may act as a stressor to trigger protective responses in plants, leading to increased resilience.
Limitations: Excess UV can damage plant tissues and reduce growth if not carefully managed.
Infrared (IR) Radiation – Beyond 800 nm
What It Is: Heat-emitting wavelengths beyond visible light.
Benefits to Plants: Infrared contributes to overall warmth, which can aid plant development in cool environments.
Limitations: Excessive infrared can overheat plants, leading to water stress or damage.
Green Light – Often Underrepresented in PAR Measurements
What It Is: 500–600 nm, technically part of PAR but often undervalued.
Role in Full Spectrum: Penetrates deeper into the plant canopy than red or blue light.
Vital for photosynthesis in lower leaves and shaded areas.
Misconception: Traditional PAR models underestimate green light’s contribution to photosynthesis.
Beyond PAR: Signals and Stress Responses
Non-Photosynthetic Effects: Wavelengths outside PAR can affect:
Circadian rhythms in plants.
Photomorphogenesis (plant shape and structure development).
Hormonal responses and stress adaptation.
Importance in Full-Spectrum Grow Lighting:
A full-spectrum light source includes UV, visible light (400–700 nm, encompassing PAR), and far-red/infrared light. This comprehensive coverage ensures:
Enhanced photosynthesis (beyond traditional PAR efficiency).
Improved plant quality (color, taste, aroma).
Support for natural plant growth cycles and stress responses.
To optimize plant health, growth, and productivity, it’s essential to balance PAR with these additional wavelengths based on the specific needs of your plants and growth stage.
As indoor gardening gains momentum, the quest for lighting solutions that emulate natural sunlight intensifies. High Color Rendering Index (CRI) LEDs emerge as a forefront solution, boasting a CRI of 90 or above, making them capable of producing light remarkably similar to natural sunlight. Ultra-high CRI LEDs, with ratings of 95 to 98, push this similarity even further, offering an unparalleled approximation of sunlight’s full spectrum.
Advantages and Challenges of High CRI LEDs
Benefits of High CRI LEDs
Natural Light Simulation: These LEDs excel in replicating the broad spectrum of sunlight, crucial for photosynthesis and overall plant health.
Energy Efficiency: High CRI LEDs outperform traditional lighting in lumens per watt, offering substantial electricity savings.
Durability: With a lifespan extending years beyond their fluorescent counterparts, these LEDs represent a long-term investment in indoor gardening.
Considerations for High CRI LEDs
Initial Cost: The upfront cost of Higher CRI LEDs can make you total system cost higher however the price gap is reducing
Heat Generation: Although they produce less heat than traditional lights, managing heat emission is still necessary for sensitive plants.
Light Spectrum: While they mimic sunlight, High CRI LEDs might not offer the exact wavelength needed for optimal plant growth, potentially necessitating supplemental lighting or nutrients.
Efficacy of High CRI LEDs in Plant Growth
The effectiveness of High CRI LEDs varies with plant species, growth stages, and required light intensity. Studies, such as those conducted by the University of Florida and the University of Arkansas, demonstrate that High CRI LEDs can surpass traditional lighting in growing lettuce, basil, and strawberries, improving both yield and quality.
Natural Sunlight Versus High CRI LEDs
Though High CRI LEDs adeptly imitate sunlight, they cannot entirely replicate its spectrum and intensity. Natural sunlight provides a more comprehensive range of wavelengths, contributing to vigorous plant growth. Nonetheless, High CRI LEDs offer a viable alternative when sunlight is unavailable, presenting a more consistent light source across seasons.
Nutrient Dynamics Under High CRI Lighting
The broad spectrum of High CRI LEDs influences plant nutrient requirements. For instance, a University of Helsinki study revealed tomato plants under High CRI lighting demanded more calcium, attributing to improved fruit quality. This indicates a shift in nutrient management strategies when transitioning from traditional to High CRI LED lighting.
Top Ten Reasons for Opting for High CRI LED Lighting
Enhanced Plant Growth: Closely mimics sunlight’s spectrum, vital for various growth stages.
Improved Visual Inspection: Easier monitoring of plant health and early detection of issues.
Increased Yield: Potential for higher production due to efficient photosynthesis.
Better Pollination Management: More natural lighting conditions could improve pollinator efficiency.
Superior Quality: Enhanced color, taste, and nutritional content of produce.
Energy Efficiency: Significant savings on electricity costs.
Extended Lifespan: Reduces the frequency of light replacement.
Lower Heat Emission: Minimizes risk to heat-sensitive plants.
Versatility: Suitable for a wide range of horticultural activities.
Environmental Benefits: Lower carbon footprint and reduced electronic waste.
In Summary, we can ask what HI CRI brings to the conversation.
Many standard grow lights use lower base CRI for example 70, 80, and 90 cri. This is a common strategy to increase efficiency. The use of newer phosphors like KSF negates the differences of efficacy in higher CRI LED’s. It’s clear that ignoring CRI as part of your lighting recipe reduces your spectrum breadth irrespective of wavelengths outside the par range, meaning use of all wavelengths in a complete lighting system that includes broad spectrum white can’t help but improve your total plant performance.
8 likes
2 comments
Share
11
Week 11. Flowering1y ago
132.08 cm
Height
12 hrs
Light Schedule
24 °C
Day Air Temp
6.7
pH
650 PPM
TDS
50 %
Air Humidity
21 °C
Substrate Temp
18 °C
Night Air Temp
378.54 liters
Pot Size
1100 PPM
CO₂ Level
Nutrients 8
Agave Nectar
1.3 mll
Honey
1.3 mll
Monopottasium Phospahte
3.91 mll
Ultraviolet The plants are deep into flower, all vegetative growth has ceased, and the only parts getting bigger are the giant fat colas! Next week, we will get to see these plants inch closer to the finish line and possibly see the beginnings of some real color expression. Onward upwards. Hard work is done for now; cool off for the next couple of weeks. All the buds are already there. They are just small. Now, I'm in preservation mode. The main priority from here on in is keeping everything cool. All about terpenes this grow. More blues, cool nights, not super saturated but still 35-40 moles.
Monopotassium Phosphate (MKP) is extensively used in agriculture as a fertilizer. Its high phosphorus content (P2O5) and potassium (K2O) make it an excellent source of these essential nutrients for plants. When dissolved in water, MKP provides readily available nutrients, which are vital for plant growth and development MKP is a nitrogen-free fertilizer, making it a good choice when nitrogen fertilization needs to be limited.
Bud factor x isn't just chitosan, it also has salicylic acid and harpin protein-all three of which stimulate systemic resistance in different ways. Bud Factor X works on your plants' immune systems, triggering their off their natural defences. It stimulates something called 'Induced Systemic Resistance' (ISR), where proteins and enzymes are released from plant cells to tackle an outside invasion. Use Advanced Nutrients Bud Factor X from week 1 of the blooming phase up to 2 weeks before the flush. Use Bud Factor X at a dosage of 2 ml/L. You can also apply Bud Factor X as a foliar spray. Bud Factor X is a powerful additive which you can mix into your water.
Induced systemic resistance (ISR) is a plant defense mechanism where beneficial microbes in the rhizosphere prime the whole plant for enhanced defense against pathogens and pests. , and this process can involve increased production of terpenoids, which are defense metabolites.
Beneficial microbes, such as certain bacteria and fungi, colonize the plant's roots and rhizosphere. These microbes trigger a systemic signaling pathway within the plant, enhancing its defenses. This priming effect leads to a more robust and rapid response when the plant is later challengedby pathogens or pests.
Rhizobacteria: Certain strains of Pseudomonas and Bacillus are known to induce ISR.
Mycorrhizal fungi: These fungi also play a role in ISR.
ISR signaling pathways are complex and involve multiple signaling molecules, including jasmonic acid, ethylene, and salicylic acid. The specific pathways involved can vary depending on the inducing microbes and the plant species.
Homework for week.
High soil salinity, a major environmental issue, arises from the accumulation of soluble salts, primarily through natural processes or human activities, leading to osmotic stress, ion toxicity, and nutrient imbalances, ultimately hindering plant growth and productivity.
Geological Features:
Salinity can be a natural feature of certain regions, particularly those with high evaporation rates and poor drainage, where salts accumulate in the soil profile over long periods.
Weathering:
The weathering of rocks and minerals releases salts into the soil, which are then transported by water.
Coastal Areas:
In coastal areas, seawater intrusion and wind-blown salt can contribute to soil salinity.
Shallow Groundwater:
When groundwater tables are shallow, water and dissolved salts can move upwards to the soil surface through capillary action, leaving salts behind as the water evaporates.
Irrigation:
Irrigation, especially with water containing high salt concentrations, can lead to the accumulation of salts in the soil, as the water evaporates and the salts are left behind
Osmotic Stress:
High salt concentrations in the soil reduce the availability of water to plants, as the osmotic potential of the soil solution becomes lower than that of the plant cells, making it difficult for plants to absorb water.
Ion Toxicity:
High concentrations of certain ions, such as sodium (Na+) and chloride (Cl-), can be toxic to plants, disrupting their metabolism and causing damage to cell structures.
Nutrient Imbalances:
Salinity can interfere with the uptake and availability of essential nutrients, leading to nutrient deficiencies in plants.
Oxidative Stress:
Salinity can trigger the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), which can damage plant cells and tissues.
Reduced Growth and Yield:
The combined effects of osmotic stress, ion toxicity, and nutrient imbalances lead to reduced plant growth, development, and yield in saline soils.
High soil salinity leads to osmotic stress in plants because the high salt concentration reduces the water potential in the soil, making it harder for plants to absorb water, even when it's present. When soil salinity increases, the concentration of dissolved salts (like sodium chloride) rises, which lowers the soil's water potential. Water naturally moves from areas of high water potential to areas of low water potential, so plants struggle to draw water from the soil into their roots when the soil's water potential is lower than the plant's. This difficulty in water uptake leads to osmotic stress, where the plant cells become dehydrated and unable to maintain turgor pressure, which is essential for cell function and growth.
Osmotic stress can cause a variety of physiological problems in plants, including:
Stomatal Closure: To conserve water, plants may close their stomata (pores on leaves), which reduces gas exchange, including carbon dioxide uptake for photosynthesis.
Reduced Photosynthesis: The stomatal closure and other effects of osmotic stress can lead to reduced photosynthetic efficiency and overall plant growth.
Nutrient Imbalances: Salt stress can interfere with nutrient absorption and transport, leading to nutrient deficiencies or toxicities.
Oxidative Stress: Salt stress can induce oxidative stress, where reactive oxygen species (ROS) accumulate, damaging plant cells and tissues.
Some plants have developed mechanisms to tolerate or mitigate salt stress, such as accumulating salt in their vacuoles, producing osmoregulatory compounds, or having enhanced antioxidant defenses. Stress, stress, stress.
Sugar and Soil Microorganisms:
Sugar, particularly in the form of glucose or other simple sugars, can serve as a carbon and energy source for soil microorganisms.
Microbial Activity and Nutrient Cycling:
When microorganisms consume sugar, they mineralize nutrients (like nitrogen) and make them more available to plants.
Soil EC is a measure of the ability of soil to conduct electricity, which is related to the concentration of dissolved ions (charged particles) in the soil solution.
Salts vs. Sugar:
Salts, like table salt, dissolve in water and break down into charged ions (cations and anions), which increases EC. Sugar, on the other hand, dissolves but doesn't dissociate into charged ions, so it doesn't directly increase EC.
Indirect Effects of Sugar:
While sugar itself doesn't directly raise EC, the increased microbial activity resulting from sugar addition can indirectly influence EC by affecting the availability of nutrients and the overall soil chemistry.
Plant health:
The sugar content of plant sap, measured as Brix, is important because it can tell us how healthy the plant is.
Sugar as a food source for microorganisms:
The idea behind adding sugar is that it is adding a food source for soil microorganisms.
In an experiment investigating the effect of salt on cannabis plant growth, high concentrations of NaCl (salt) led to reduced growth, impaired photosynthesis, and decreased cannabinoid content, while lower concentrations had less impact, and some even showed a slight increase in certain cannabinoid types.
In some studies, higher salinity levels led to a predominance of cannabidiol (CBD) compared to lower salinity levels.
Potential for Biostimulants:
Plant-based biostimulants (like legume protein hydrolysate) may help mitigate the detrimental effects of saline irrigation on crop growth and phytocannabinoid composition.
11 likes
1 comment
Share
12
Week 12. Flowering1y ago
137.16 cm
Height
12 hrs
Light Schedule
24 °C
Day Air Temp
6.4
pH
50 %
Air Humidity
19 °C
Substrate Temp
18 °C
Night Air Temp
378.54 liters
Pot Size
900 PPM
CO₂ Level
Nutrients 3
Agave
5.21 mll
Honey
3.91 mll

RAW Cane Molasses
10.42 mll
Ultraviolet Boron plays a role in the formation of sugar complexes for translocation within plants, and in the formation of proteins. Aids in the production of sugars and carbohydrates, and is essential for seed and fruit development. Enhances the uptake of calcium, magnesium, and potassium, and enables sugar translocation. Boron is an essential micronutrient for plant growth, and deficiencies can lead to decreased water absorption, root growth, and sugar translocation.
They are formed in the cell sap inside the vacuole when sugars combine with complex compounds called anthocyanidins. Anthocyanin production is influenced by factors like light intensity and sugar concentration in the sap, sucrose is highly mobile in plants and serves as the primary form of carbohydrate transported long distances from source tissues (like leaves) to sink tissues (like roots, stems, and developing organs) via the phloem. While plants produce glucose through photosynthesis, for long-distance transport, glucose is primarily converted into and transported as sucrose, not glucose itself. Sucrose is a more efficient form for long-distance transport and storage because it's a non-reducing sugar, meaning it doesn't react readily with other molecules, and it contains more energy per molecule than glucose. Plants store excess glucose as starch, a complex carbohydrate, for later use as an energy source. Glucose also functions as a signaling molecule, conveying the plant's metabolic status and influencing growth, development, and survival. Plants can absorb sucrose through foliar sprays, and studies show that foliar application of sucrose can increase soluble sugar content and potentially improve plant growth and yield. Sucrose is the primary form of sugar transported throughout plants, acting as a source of carbon and energy for non-photosynthetic organs. While foliar application of sucrose can be beneficial, it's important to note that there can be a concentration effect, with high concentrations potentially decreasing soluble sugar content. The cuticular pathway (the outer layer of the leaf) has a low size exclusion limit, allowing for the diffusion of small carbohydrates like sucrose. Stomata (pores on the leaf surface) also allow for the entry of larger molecules, including sucrose.
Plant roots can absorb sucrose, but they primarily rely on the import of sugar from the aerial parts (leaves) via the phloem, and they can also absorb monosaccharides like glucose and fructose.
https://www.chem.ualberta.ca/~vederas/Chem_263/outlines/pdf/Chem263%20Nov%2022%202016%20notes.pdf
Sugar is the generic name for sweet-tasting, soluble carbohydrates, many of which are used in food. Simple sugars, ... (G3P), a phosphated 3-carbon sugar that is used by the cell to make monosaccharides such as glucose (C 6 H 12 O 6) or (as in cane and beet) sucrose (C 12 H 22 O 11). The carbonyl carbon becomes the anomeric carbon in the ring by binding to the oxygen of a hydroxyl elsewhere in the chain. α- and β- forms of a given sugar can readily "flip" between each form in solution, so long as the anomeric hydroxyl is free, because the bonding in cyclic forms is unstable.
Glucose:Plants synthesize glucose during photosynthesis, which is a simple sugar.
Sucrose:Glucose can be converted into sucrose, a more complex sugar, and is the main form in which sugars are transported through the plant's phloem (vascular tissue).
Plants transport sucrose, not glucose, because sucrose is a more stable, non-reactive disaccharide that is more energy-efficient for long-distance transport and storage compared to glucose, a reactive monosaccharide.
Energy Efficiency:
Sucrose is a disaccharide (glucose + fructose), containing more energy per molecule than a monosaccharide like glucose. This makes it a more efficient form for transport and storage of energy throughout the plant.
Reduced Reactivity:
Sucrose is a non-reducing sugar, meaning it's less prone to reactions with other molecules during transport. This stability is crucial for ensuring the sugar reaches its destination in the plant without being altered or consumed along the way.
Phloem Transport:
The phloem, the plant's vascular tissue responsible for transporting sugars, is specifically adapted for the transport of sucrose.
Sucrose is synthesized in photosynthetically active cells from fructose and glucose and is then transported via the phloem to heterotrophic parts of the plant.
I added powdered cane molasses to the soil and watered it with agave nectar and honey bubble tea. Lower temperatures are leading to slower transpiration, and the medium is not drying as fast as it was before, which increases moisture retention.
Cane Mollases is a byproduct of sugar cane processing, primarily breaks down into the sugars sucrose, glucose, and fructose.
Sucrose: This is a disaccharide (two sugar molecules linked together) that is the most abundant sugar in molasses.
Glucose and Fructose: These are monosaccharides (single sugar molecules) that are also present in molasses, although in smaller amounts than sucrose.
Agave nectar primarily consists of fructose and glucose, with fructose making up a significantly larger portion (around 80-90%).
Fructose: Agave nectar is known for its high fructose content, which contributes to its sweetness and lower glycemic index compared to table sugar.
Glucose: While fructose is the dominant sugar, glucose is also present, though in much smaller amounts (around 20%). In addition to fructose and glucose, agave syrup contains water, small amounts of other carbohydrates, fat, polyols, vitamins, and minerals.
Honey primarily consists of the simple sugars fructose and glucose, along with smaller amounts of other sugars like sucrose and maltose.
Fructose and Glucose: These are the two main monosaccharides (simple sugars) found in honey, making up about 80% of its composition.
Sucrose: A disaccharide (two simple sugars linked together), made of fructose and glucose, is also present in honey.
Maltose: Another disaccharide, made of two glucose molecules, is found in smaller amounts.
Other Sugars: Honey also contains a variety of other sugars, including oligosaccharides, which are chains of two or more simple sugars.
Water: Honey contains a significant amount of water, around 17-20%.
Non-sugar components:Aside from sugars and water, honey contains a small amount of vitamins, minerals, and other compounds.
Plant senescence, or aging and decline, is strongly linked to sugar levels, with both sugar accumulation and starvation playing roles in the process, depending on the context and plant species. Besides age-dependent/developmental senescence, environmental conditions can also trigger senescence, and it has been shown that the timing and rate of senescence is highly affected by environmental cues such as photoperiod, temperature, and moisture in soil.
There has been some debate whether leaf senescence is induced by sugar starvation or by sugar accumulation. External supply of sugars has been shown to induce symptoms of senescence such as leaf yellowing. However, it was so far not clear if sugars have a signalling function during developmental senescence. Glucose and fructose accumulate strongly during senescence in Arabidopsis thaliana (L.) Heynh. leaves. Using Affymetrix GeneChip analysis we determined the effect of sugar-induced senescence on gene expression. Growth on glucose in combination with low nitrogen supply induced leaf yellowing and changes in gene expression that are characteristic of developmental senescence. Most importantly, the senescence-specific gene SAG12, which was previously thought to be sugar-repressible, was induced over 900-fold by glucose.
Carbon and nitrogen are important sources that are released during the senescence process or remobilized to other growing parts of plants. Sugars (glucose and fructose) accumulate during stress and in naturally senesced leaves.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16514542/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16157653/
Developmental leaf senescence, the natural aging and decline of leaves, is influenced by sugar signaling pathways, where sugars like glucose and fructose, accumulated in old leaves, act as signals for carbon availability, potentially triggering senescence.
Sugar as a Senescence Signal:
In plants, sugar accumulation, particularly in old leaves, can signal an excess of carbon relative to nitrogen.
This excess carbon, or high sugar levels, can trigger the onset of leaf senescence, a process involving the degradation of macromolecules, loss of photosynthetic activity, and nutrient remobilization.
Sugar signaling plays a crucial role in coordinating environmental conditions with the availability of internal carbohydrates, influencing developmental transitions like flowering and senescence.
Key Players in Sugar Signaling:
Hexokinase (HXK): HXK acts as a glucose signaling sensor and plays a role in regulating leaf senescence.
SnRK1 (Sucrose Non-Fermenting 1-Related Protein Kinase 1): SnRK1 is a kinase that can delay senescence by communicating sugar demand by the sink and ensuing sugar transport from the source.
TOR (Target of Rapamycin): TOR kinase is another central regulator of carbon status and energy sensors that operate antagonistically in regulating sugar-responsive genes.
Sugar Signaling Pathways:
Hexose-dependent pathways: Plants possess intracellular and extracellular sugar sensors, and the regulator of G-protein signaling 1 (RGS1) plays a critical role as an external sugar sensor.
Disaccharide signaling pathways: Sucrose is the main sugar for systemic source-to-sink transport in plants, and non-metabolizable sucrose analogs can mimic the effect of sucrose.
Examples of Sugar-Induced Senescence:
Nitrogen Deficiency: Under low nitrogen availability, sugar accumulation can induce leaf senescence.
High Light: Growth in high light conditions can also lead to sugar accumulation and senescence.
Glucose Accumulation: The presence of glucose in the growth medium, especially under low nitrogen conditions, can induce leaf yellowing and up-regulation of senescence-associated genes (SAGs).
Sugar-induced Senescence: External supply of sugars has been shown to induce symptoms of senescence such as leaf yellowing.
While the role of sugars in senescence is well-established, the underlying molecular mechanisms and the crosstalk between sugar and other signaling pathways are still being investigated.
8 likes
2 comments
Share
13
Week 13. Flowering1y ago
139.7 cm
Height
12 hrs
Light Schedule
24 °C
Day Air Temp
6.3
pH
650 PPM
TDS
50 %
Air Humidity
19 °C
Substrate Temp
17 °C
Night Air Temp
378.54 liters
Pot Size
800 PPM
CO₂ Level
Ultraviolet Metals in general reflect all of the light energy that comes onto them but copper doesn't reflect all of them. It absorbs part of the spectrum. It absorbs the blue part of the light and maybe some of the green light and reflects all the coppery colored light which comes back into our eyes. That's what happens with the metal.
The green pigment in leaves is chlorophyll, which absorbs red and blue light from sunlight. Therefore, the light the leaves reflect is diminished in red and blue and appears green. The molecules of chlorophyll are large (C55H70MgN4O6). They are not soluble in the aqueous solution that fills plant cells. Instead, they are attached to the membranes of disc-like structures, called chloroplasts, inside the cells. Chloroplasts are the site of photosynthesis, the process in which light energy is converted to chemical energy. In chloroplasts, the light absorbed by chlorophyll supplies the energy used by plants to transform carbon dioxide and water into oxygen and carbohydrates, which have a general formula of Cx(H2O)y.
In this endothermic transformation, the energy of the light absorbed by chlorophyll is converted into chemical energy stored in carbohydrates (sugars and starches). This chemical energy drives the biochemical reactions that cause plants to grow, flower, and produce seed.
Chlorophyll is not a very stable compound; bright sunlight causes it to decompose. To maintain the amount of chlorophyll in their leaves, plants continuously synthesize it. The synthesis of chlorophyll in plants requires sunlight and warm temperatures. Therefore, during summer chlorophyll is continuously broken down and regenerated in the leaves.
Another pigment found in the leaves of many plants is carotene. Carotene absorbs blue-green and blue light. The light reflected from carotene appears yellow. Carotene is also a large molecule (C40H36) contained in the chloroplasts of many plants. When carotene and chlorophyll occur in the same leaf, together they remove red, blue-green, and blue light from sunlight that falls on the leaf. The light reflected by the leaf appears green. Carotene functions as an accessory absorber. The energy of the light absorbed by carotene is transferred to chlorophyll, which uses the energy in photosynthesis. Carotene is a much more stable compound than chlorophyll. Carotene persists in leaves even when chlorophyll has disappeared. When chlorophyll disappears from a leaf, the remaining carotene causes the leaf to appear yellow.
A third pigment, or class of pigments, that occur in leaves are the anthocyanins. Anthocyanins absorb blue, blue-green, and green light. Therefore, the light reflected by leaves containing anthocyanins appears red. Unlike chlorophyll and carotene, anthocyanins are not attached to cell membranes but are dissolved in the cell sap. The color produced by these pigments is sensitive to the pH of the cell sap. If the sap is quite acidic, the pigments impart a bright red color; if the sap is less acidic, its color is more purple. Anthocyanin pigments are responsible for the red skin of ripe apples and the purple of ripe grapes. A reaction between sugars and certain proteins in cell sap forms anthocyanins. This reaction does not occur until the sugar concentration in the sap is quite high. The reaction also requires light, which is why apples often appear red on one side and green on the other; the red side was in the sun and the green side was in shade.
During summer, the leaves are factories producing sugar from carbon dioxide and water using by the action of light on chlorophyll. Chlorophyll causes the leaves to appear green. (The leaves of some trees, such as birches and cottonwoods, also contain carotene; these leaves appear brighter green because carotene absorbs blue-green light.) Water and nutrients flow from the roots, through the branches, and into the leaves. Photosynthesis produces sugars that flow from the leaves to other tree parts where some of the chemical energy is used for growth and some is stored. The shortening days and cool nights of fall trigger changes in the tree. One of these changes is the growth of a corky membrane between the branch and the leaf stem. This membrane interferes with the flow of nutrients into the leaf. Because the nutrient flow is interrupted, the chlorophyll production in the leaf declines and the green leaf color fades. If the leaf contains carotene, as do the leaves of birch and hickory, it will change from green to bright yellow as the chlorophyll disappears. In some trees, as the sugar concentration in the leaf increases, the sugar reacts to form anthocyanins. These pigments cause the yellowing leaves to turn red. Red maples, red oaks, and sumac produce anthocyanins in abundance and display the brightest reds and purples in the fall landscape.
The range and intensity of autumn colors is greatly influenced by the weather. Low temperatures destroy chlorophyll, and if they stay above freezing, promote the formation of anthocyanins. Bright sunshine also destroys chlorophyll and enhances anthocyanin production. Dry weather, by increasing sugar concentration, also increases the amount of anthocyanin. So the brightest autumn colors are produced when dry, sunny days are followed by cool, dry nights. The secret recipe. Nature knows best. Normally I'd keep a 10-degree swing between day and night but ripening will see the gap increase dramatically on this one.
Anthocyanin color is highly pH-sensitive, turning red or pink in acidic conditions (pH 7)
Acidic Conditions (pH 7):
Anthocyanins tend to change to bluish or greenish colors, and in very alkaline solutions, they can become colorless as the pigment is reduced.
The color changes are due to structural transformations of the anthocyanin molecule in response to pH changes, involving the protonation and deprotonation of phenolic groups.
Anthocyanins, responsible for red, purple, and blue colors in plants, differ from other pigments like carotenoids and chlorophylls because their color changes with pH, making them unique pH indicators, while other pigments are more stable in color. Anthocyanins are a whole family of plant pigments. They are present in lilac, red, purple, violet or even black flower petals. Anthocyanins are also found in fruits and vegetables, as well as some leaves. Cold weather causes these purple pigments to absorb sunlight more intensely, which, in turn, raises the core temperature of the plant compared to that of the ambient air. This protects the plant from cold temperatures. In hot weather or at high altitudes, anthocyanins protect the plant cells by absorbing excessive ultraviolet radiation. Furthermore, a vivid petal coloration makes it easier for insects to find the flowers and pollinate them.
Adding NaHSO4 (sodium hydrogen sulfate) to water increases the number of protons H+ in the solution. In other words, we increase the acidity of the medium because sodium hydrogen sulfate dissociates in water, or, in other words, it breaks down into individual ions:
NaHSO4 → HSO4- + Na+
HSO4- SO42- + H+
In turn, the H+ protons react with the anthocyanin molecules transforming them from the neutral into cationic form. The cationic form of anthocyanins has a bright red color.
The color of anthocyanins is determined by the concentration of hydrogen ions H+. When we add the sodium carbonate Na2CO3 solution, the H+ concentration drops. A decrease in the number of H+ causes a pigment color change, first to purple and then to blue and dark green.
Anthocyanins are unstable in a basic environment, and so they gradually decompose. The decomposition process produces yellow-colored substances called chalcones. This process is quite slow, allowing us to track how a solution changes its color from blue to various shades of green and finally to yellow.
The best petals would be brightly colored dark petals of red, purple, blue, or violet. You are particularly lucky if you can get your hands on almost black petals from either petunia, roses, irises, African violets, tulips, or lilies. These flowers contain a maximum concentration of anthocyanins.
British scientist Robert Boyle (1627–1691) made a number of remarkable discoveries in chemistry. Interestingly, one of these discoveries involved the beautiful flowers known as violets.
One day, Boyle brought a bouquet of violets to his laboratory. His assistant, who was performing an experiment at the time, accidentally splashed some hydrochloric acid on the flowers. Worried that the acid would harm the plants, the assistant moved to rinse them with water, but Boyle suddenly stopped him.
The scientist’s attention was fixed on the violets. The places where acid had splashed the petals had turned from purple to red. Boyle was intrigued. “Would alkalis affect the petals, too?” he wondered and applied some alkali to a flower. This time the petals turned green! Experimenting with different plants, Boyle observed that some of them changed colors when exposed to acids and alkalis. He called these plants indicators.
By the way, the violet color of the petals is produced by anthocyanins – pigments that absorb all light waves except violet. These vibrant pigments help attract bees, butterflies, and other pollinators, facilitating the flower’s reproduction.
Anthocyanins are a type of flavonoid, a large class of plant pigments. They are derived from anthocyanidins by adding sugars.
Sugars, particularly sucrose, are involved in signaling networks related to anthocyanin biosynthesis, and sucrose is a strong inducer of anthocyanin production in plants.
Sugar-boron complexes, also known as sugar-borate esters (SBEs), are naturally occurring molecules where one or two sugar molecules are linked to a boron atom, and the most studied example is calcium fructoborate (CaFB).
Boron is a micronutrient crucial for plant health, playing a key role in cell wall formation, sugar transport, and reproductive development, and can be deficient in certain soils, particularly well-drained sandy soils.
Narrow Range:
There's a small difference between the amount of boron plants need and the amount that causes toxicity. Soil concentrations greater than 3 ug/ml (3ppm) may indicate potential for toxicity.
Anthocyanins, the pigments responsible for the red, purple, and blue colors in many fruits and vegetables, are formed when an anthocyanidin molecule is linked to a sugar molecule through a glycosidic bond.
Glycosidic bonds are covalent linkages, specifically ether bonds, that connect carbohydrate molecules (saccharides) to other groups, including other carbohydrates, forming larger structures like disaccharides and polysaccharides.
Formation:
Glycosidic bonds are formed through a condensation reaction (dehydration synthesis) where a water molecule is removed, linking the hemiacetal or hemiketal group of one saccharide with the hydroxyl group of another molecule.
Types:
O-glycosidic bonds: The most common type, where the linkage involves an oxygen atom.
N-glycosidic bonds: Less common, but important, where the linkage involves a nitrogen atom.
Orientation:
Glycosidic bonds can be alpha or beta, depending on the orientation of the anomeric carbon (C-1) of the sugar.
Alpha (α): The hydroxyl group on the anomeric carbon is below the ring plane.
Beta (β): The hydroxyl group on the anomeric carbon is above the ring plane.
Disaccharides: Lactose (glucose + galactose), sucrose (glucose + fructose), and maltose (glucose + glucose) are examples of disaccharides linked by glycosidic bonds.
Polysaccharides: Starch (amylose and amylopectin) and glycogen are polysaccharides formed by glycosidic linkages between glucose molecules.
Significance:
Glycosidic bonds are crucial for forming complex carbohydrates, which play vital roles in energy storage, structural support (like in cell walls), and as components of important biomolecules like glycoproteins and glycolipids.
9 likes
comments
Share
14
Week 14. Flowering1y ago
139.7 cm
Height
12 hrs
Light Schedule
24 °C
Day Air Temp
6.3
pH
350 PPM
TDS
45 %
Air Humidity
18 °C
Substrate Temp
17 °C
Night Air Temp
378.54 liters
Pot Size
800 PPM
CO₂ Level
Nutrients 3

Bud Factor X
3 mll

RAW Amino Acids
0.26 mll

RAW Enzymes
0.26 mll
Ultraviolet For last week she had been receiving a light foliar application of aminos/sucrose 20-30 min prior to lights on.
Plants do store nutrients in their stems, alongside their roots and leaves, acting as a vital storage and transport hub for water, nutrients, and sugars. Roots absorb water and nutrients from the soil and also store nutrients.
Leaves are the main photosynthetic organs, but they also store some nutrients. 😒 🤔
At night, when stomata shut and transpiration stops, the water is held in the stem and leaf by the adhesion of water to the cell walls of the xylem vessels and tracheids, and the cohesion of water molecules to each other. This is called the cohesion–tension theory of sap ascent.
( Pyroligneous Vinegar )
Organic Acids:
Pyroligneous vinegar contains organic acids that can dissolve phosphorus and make it more available for plant uptake.
Antimicrobial Properties:
The compounds in pyroligneous vinegar can inhibit the growth of plant pathogens and pests.
Biostimulant:
It can act as a biostimulant, promoting plant growth and development.
Soil Microorganisms:
Pyroligneous vinegar can increase the metabolic activity of microorganisms in the soil, which are important for nutrient cycling and soil health.
Adequate soil moisture is crucial for plant photosynthesis, nutrient uptake, and overall growth, which directly impacts carbon assimilation by plants.
A moderate level of soil moisture supports the activity of beneficial soil microorganisms that decompose organic matter, releasing nutrients and contributing to carbon cycling.
Optimal moisture levels enhance the processes of carbon sequestration, where carbon is stored in the soil as organic matter, effectively removing it from the atmosphere.
Plants use carbon dioxide and water to produce sugars through photosynthesis. These sugars are then used as energy and building blocks for plant growth, and can also be stored in the soil as organic matter.
The decomposition of plant and microbial residues releases carbon back into the soil and atmosphere. Soil moisture plays a crucial role in regulating this process, influencing the rate of decomposition and the form in which carbon is released.
Excessive Soil Moisture:
Reduced Oxygen: Saturated soil conditions can lead to a lack of oxygen, which can inhibit microbial activity and potentially lead to the release of greenhouse gases like methane.
Decomposition: While some decomposition occurs in saturated soils, the process can be slowed down, leading to a build-up of organic matter and potentially reducing the availability of nutrients for plants.
Insufficient Soil Moisture:
Water Stress: Drought conditions can cause water stress in plants, leading to reduced photosynthesis and carbon uptake.
Reduced Microbial Activity: Dry soils can also limit microbial activity, reducing the decomposition of organic matter and nutrient cycling.
Carbon sequestration refers to the process of capturing and storing atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2) in long-term storage, like in soils and plants.
Adding carbon to soil, through practices like cover cropping and using organic amendments, does not eliminate the need for carbon sequestration, but it is a crucial component of a broader strategy to increase carbon storage in soil
Planting cover crops (like clover, beans, and peas) after the main crop is harvested helps soils take in carbon year-round, and these crops can be plowed under as "green manure" to add more carbon to the soil.
Increased soil carbon improves soil structure, water retention, and nutrient availability, leading to healthier and more productive soils.
Healthy soils with high carbon content are more resilient to drought, erosion, and other environmental stresses.
Chemical degradation and soil deterioration is a global issue, mainly caused by the wide scale application of synthetic fertilizers. Adding activated charcoal allows oxygen to be redistributed to the soil, allowing for plant roots to thrive.
Biochar: Primarily used as a soil amendment to improve soil structure, water retention, and nutrient availability, as well as for carbon sequestration.
Activated Charcoal: Widely used for filtration and adsorption, such as in water purification, air purification, and as a medicinal agent (e.g., to absorb toxins).
Key Differences: Porosity and Surface Area: Biochar generally has a lower porosity and surface area compared to activated charcoal, which is specifically engineered for high porosity and surface area.
Ion Exchange Capacity: Biochar exhibits a significant amount of ion exchange capacity, which is minimal or absent in traditional activated carbons.
pH: Activated charcoal is more alkaline than biochar, with a pH range of 9-11.
Similarities:Both biochar and activated charcoal are carbon-based materials produced through pyrolysis. Both can be used as adsorbents, but their primary applications differ significantly.
One specific form of C60, carboxylated fullerene C60[C(COOH)2]3, . Activated Charcoal increases soil fertility and plant growth rate.
Biochar:
Biochar, a type of charcoal produced through pyrolysis (heating organic matter in the absence of oxygen), is often used as a soil amendment.
To maximize its benefits, biochar is often "charged" or inoculated with nutrients and microbes before being applied to the soil.
"Charging" involves mixing biochar with organic matter like compost, worm castings, or fertilizer, allowing the biochar to absorb these nutrients and microbes.
This process ensures that the biochar can effectively hold and release nutrients to plants and microbes in the soil.
Biochar's porous structure allows it to act as a reservoir for nutrients and water, improving soil health and fertility.
Activated Charcoal:
Activated charcoal, also known as activated carbon, is a form of charcoal that has been treated to increase its porosity and surface area.
It's primarily used for filtration and adsorption, meaning it's effective at removing impurities from water and air.
The porous structure of activated charcoal allows it to bind to various molecules, including toxins and gases.
Activated charcoal doesn't require the same "charging" process as biochar because its primary function is to adsorb rather than to provide nutrients.
While activated charcoal can be used in soil applications, its primary purpose is for filtration and purification rather than soil amendment.
Biochar:
Biochar, a type of charcoal produced through pyrolysis (heating organic matter in the absence of oxygen), is often used as a soil amendment.
To maximize its benefits, biochar is often "charged" or inoculated with nutrients and microbes before being applied to the soil.
"Charging" involves mixing biochar with organic matter like compost, worm castings, or fertilizer, allowing the biochar to absorb these nutrients and microbes.
This process ensures that the biochar can effectively hold and release nutrients to plants and microbes in the soil.
Biochar's porous structure allows it to act as a reservoir for nutrients and water, improving soil health and fertility.
Activated Charcoal:
Activated charcoal, also known as activated carbon, is a form of charcoal that has been treated to increase its porosity and surface area.
It's primarily used for filtration and adsorption, meaning it's effective at removing impurities from water and air.
The porous structure of activated charcoal allows it to bind to various molecules, including toxins and gases.
Activated charcoal doesn't require the same "charging" process as biochar because its primary function is to adsorb rather than to provide nutrients.
While activated charcoal can be used in soil applications, its primary purpose is for filtration and purification rather than soil amendment.
12 likes
comments
Share
15
Week 15. Harvest10mo ago
Happy Harvest Day!

10/10
Rated
Very strong genetics again from PC, thank you.
Show more
Translate
Spent 93 days
Ger Veg Flo Har
142.5 g
Bud dry weight per plant
4
Plants
10.16 m²
Grow Room size
Normal
Difficulty

Relaxed, Uplifted, Hungry
Positive effects

Cream, Citrus, Berries
Taste
Height
Day air temperature
Air humidity
PPM
PH
CO2
Light schedule
Night air temperature
Substrate temperature
Pot size
Lamp distance
Ultraviolet Lips of wisdom are closed but to the ears of understanding.
14 likes
12 comments
Share
Equipment Reviews

the end.
Enjoying this diary? Follow for more updates!
Prefer the old Diary view?
Go back to the old Diary view